A compagny that has been collecting songs' data and users activity wants an efficient model to store and analyze the data. The data currently resides in folders in JSON format. This project consists of creating a database and build an ETL pipeline to store the data. This will help the analytics to analyze and derive insights from data.
There are two sources of dataset, the Song Dataset and the Log Dataset . Both dataset are currently stored in amazon S3. These files will be read from redshift and stored in some staging tables. Then another process will extract the data from staging tables and load in final tables.
The song data is stored at : s3://udacity-dend/song_data
This is a collection of JSON data that store songs data. The files are partitioned by the three letters of of each song's track ID. These are two examples:
- song_data/A/B/C/TRABCEI128F424C983.json
- song_data/A/A/B/TRAABJL12903CDCF1A.json
Each file is structured as:
{"num_songs": 1, "artist_id": "ARJIE2Y1187B994AB7", "artist_latitude": null, "artist_longitude": null, "artist_location": "", "artist_name": "Line Renaud", "song_id": "SOUPIRU12A6D4FA1E1", "title": "Der Kleine Dompfaff", "duration": 152.92036, "year": 0}
The Log dataset is stored at Log data: s3://udacity-dend/log_data and the JSON path is s3://udacity-dend/log_data.
The second dataset is a set of JSON log files generated by an event similator base of songs dataset above. These files simulate activity logs partitioned by year and month as we can see below:
- log_data/2018/11/2018-11-12-events.json
- log_data/2018/11/2018-11-13-events.json
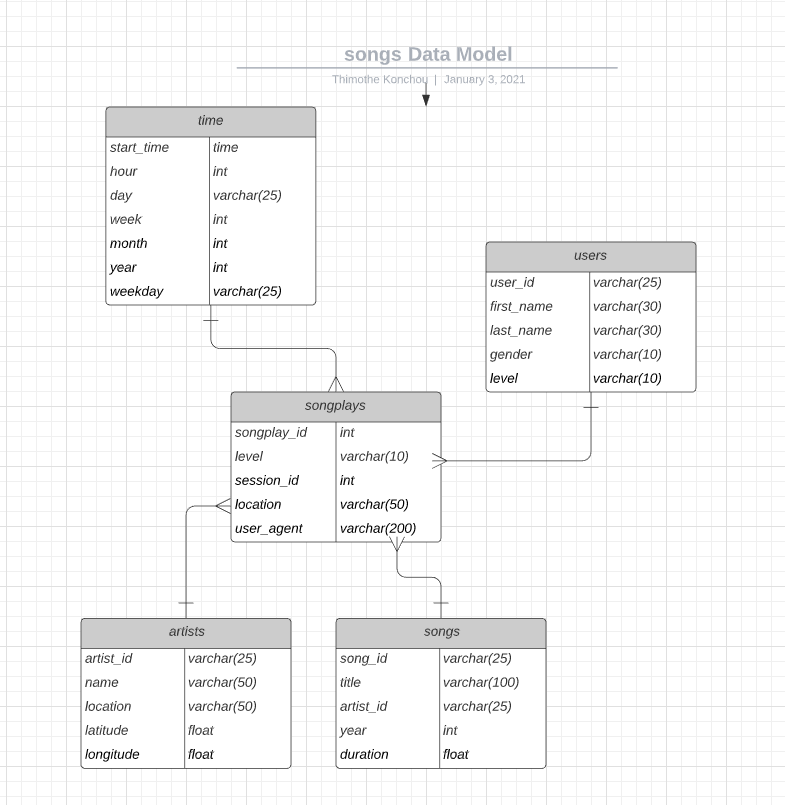
For this project, we will building a star model with fact and dimension tables. This schema is analytic focus as all dimensions tables are one join away from that fact tables that easier queries retrieval. Here is tables description:
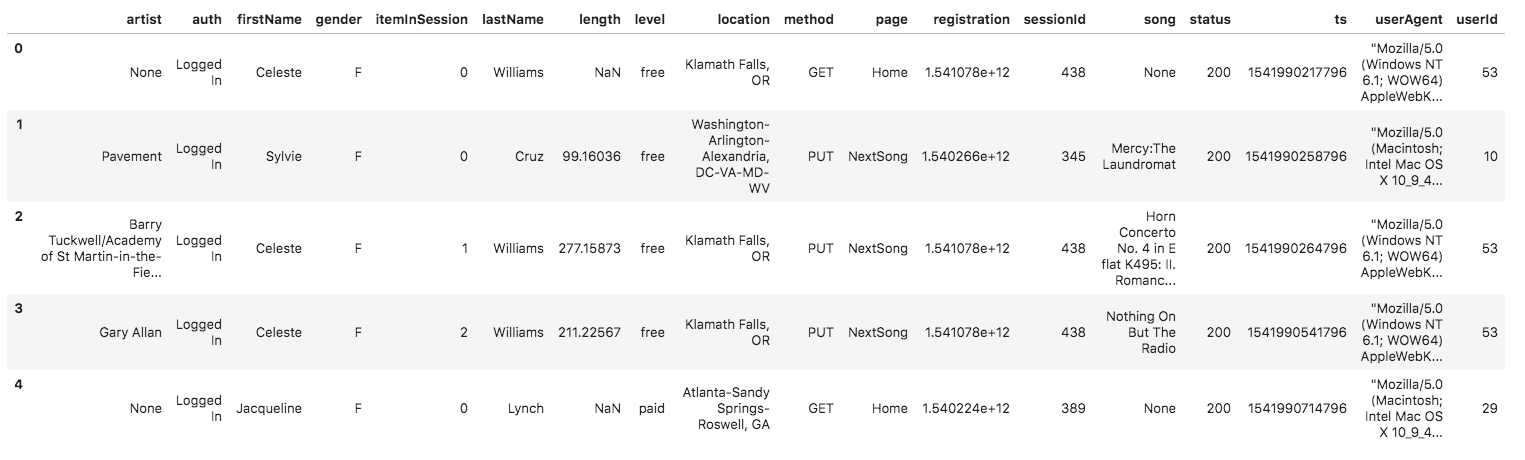
The staging tables will store all fields as they are from the files in S3
- staging events table
'staging_events
artist
auth
firstName gender
itemInSession lastName
length
level location method page registration sessionId song status igint, ts
userAgent userId
' - staging songs tables
staging_songs num_songs artist_id artist_latitude artist_longitude artist_location artist_name song_id title duration year
Fact Table
1 - songplays - records in log data associated with song plays i.e. records with page NextSong
songplay_id, start_time, user_id, level, song_id, artist_id, session_id, location, user_agent
Dimension Tables
2 - users - users in the app
user_id, first_name, last_name, gender, level
3 - songs - songs in music database
song_id, title, artist_id, year, duration
4- artists - artists in music database
artist_id, name, location, latitude, longitude
5- time - timestamps of records in songplays broken down into specific units
start_time, hour, day, week, month, year, weekday
The project has multiple files, here is the description:
1- test.ipynb : displays the first few rows of each table to let you check your database.
2- create_tables.py : drops and creates your tables. You run this file to reset your tables before each time you run your ETL scripts.
3- etl.ipynb : reads and processes a single file from song_data and log_data and loads the data into your tables. This notebook contains detailed instructions on the ETL process for each of the tables.
4 - etl.py : reads and processes files from song_data and log_data and loads them into your tables. You can fill this out based on your work in the ETL notebook.
5 - sql_queries.py : contains all your sql queries, and is imported into the last three files above.
- Install python 3.8
- Clone the current repository
- Launch a redshift cluster and create an IAM role that has read access to S3
- Add redshift database and IAM role info to dwh.cfg
- Open command line and move to the repository folder
- Run the
create_tables.pyfile to drop and create the database as well as all tables - Run the
etl.pyfile to read, extract, transform and load data to different tables
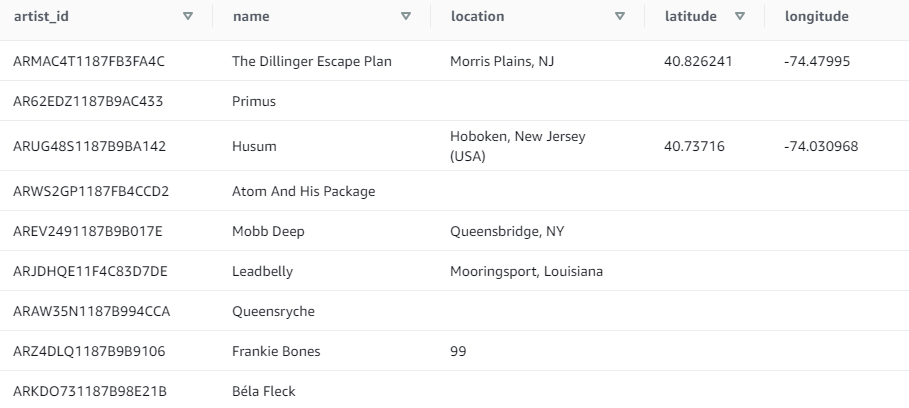
- First 10 artists:
select * from artists where limit 10;
Result:
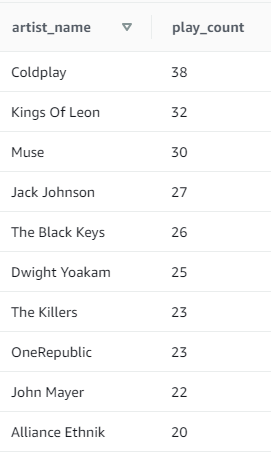
- 10 most popular artists:
SELECT name as artist_name ,COUNT(DISTINCT session_id) as play_count FROM songplays s JOIN artists a ON a.artist_id = s.artist_id WHERE level='paid' GROUP BY name ORDER BY play_count DESC LIMIT 10;
Result: