ROS is a framework that allows developers to create and manage robotic systems using a variety of tools and libraries. This includes publisher and subscriber features for data communication, action clients for making requests to a server, launch files for starting and configuring nodes, custom services for creating new request-response patterns, and custom messages for sending data between nodes. All of these features work together to enable communication between different parts of a robotic system, making it easy to create, test, and launch complex robotic applications.
- scrpits: node (a),node (b), node (c)
- msg: counter.msg, cont.msg
- launch.file: Includes the launch.file for the globe simulator and every node.
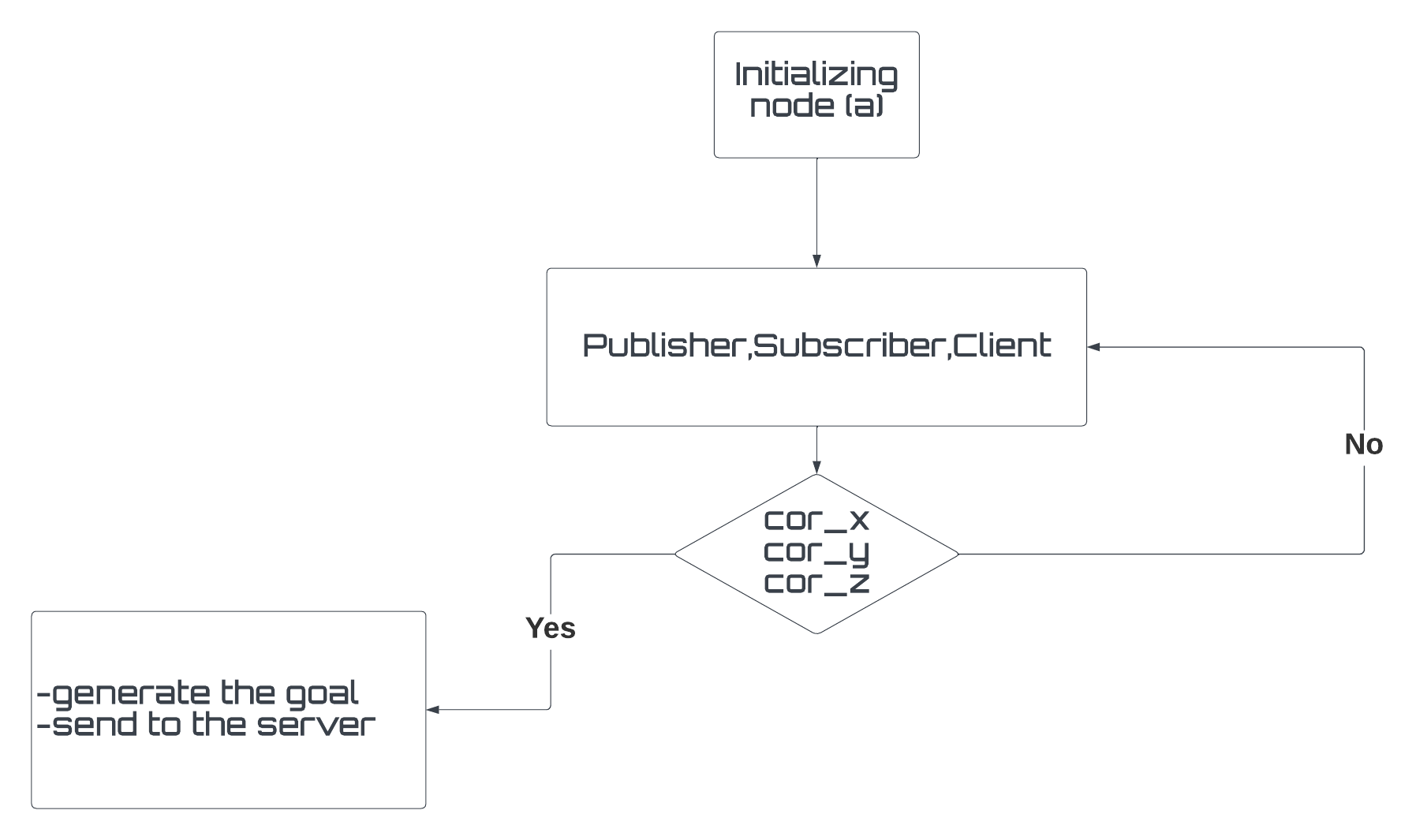
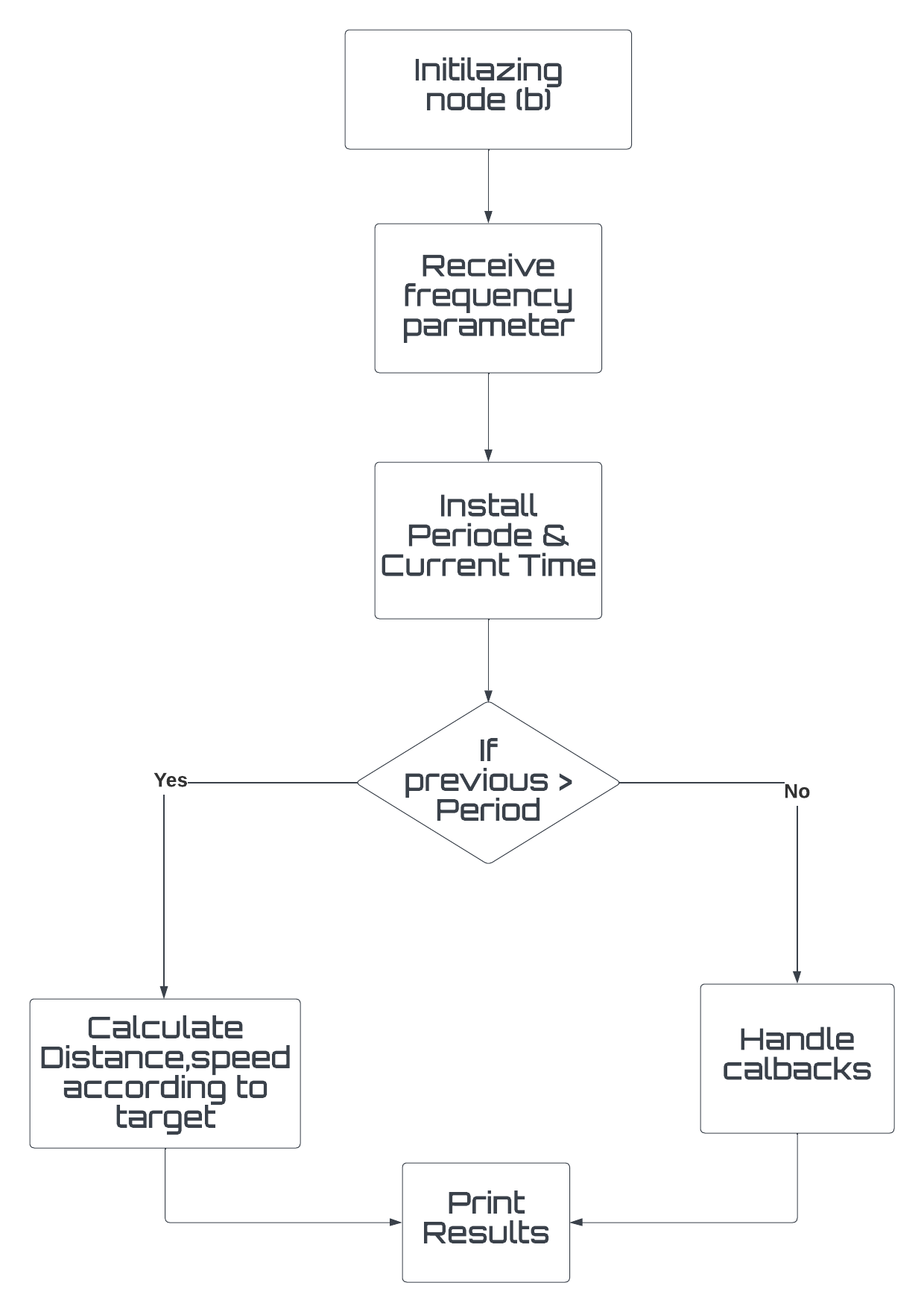
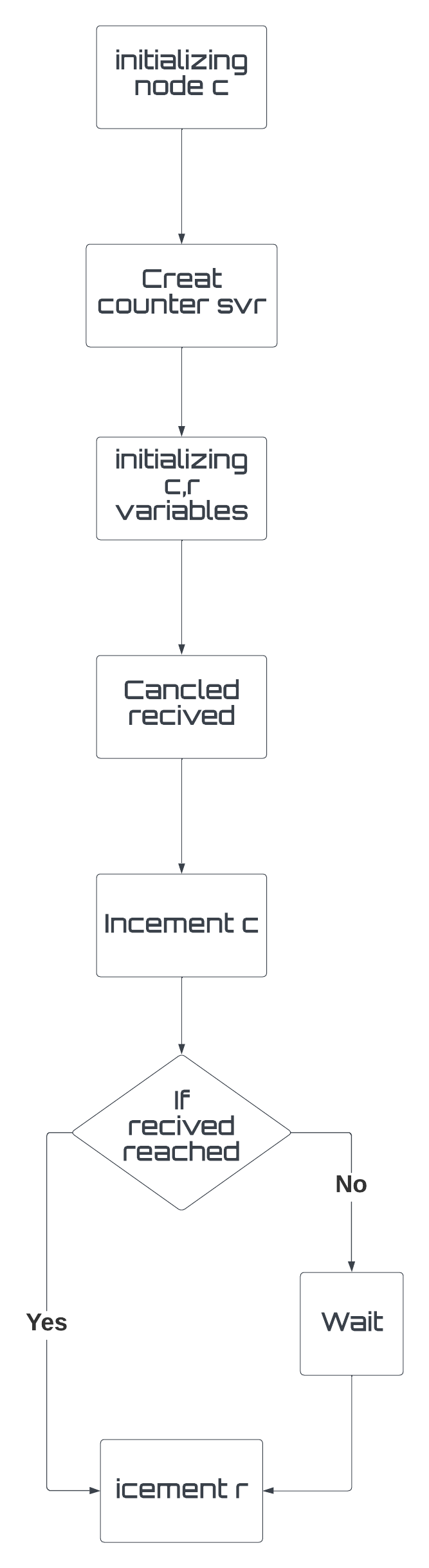
node (a) called "Control" that retrieves user input and sets a goal, node (b) called "robot_info" that calculates the average speed and distance, and node (c) called "Counter" that counts the number of goals reached and canceled. There is also a custom message called "vel_position" located in the "/msg" directory that allows node (b) to calculate the distance and average velocity assigned by the robot.
Additionally, there is a customized service called "count.srv" located in the "assignment_2_2022/srv" directory that takes in canceled and reached goals by the robot and the user. The launch file "assignment1.launch" located in the "assignment_2_2022" directory starts all of the nodes and the world simulator.
To run the program, first build the world by inserting "catkin_make", then launch the ROS by pressing "assignment_2 assignment1.launch". The user interface prompts the user to insert their desired position X and Y, or to cancel by pressing "Cancel".
The flowchart of the program shows the sequence of actions taken by the nodes. Node (a) retrieves user input and sets a goal, which is then passed to node (b) to calculate the average speed and distance. Node (c) counts the number of goals reached and canceled.