Releases: QoderAI/blog
Repo Wiki: Surfacing Implicit Knowledge
desc: Turn code into living, shared documentation.
category: Product
img: https://img.alicdn.com/imgextra/i2/O1CN01c6LKGp1NGHqns4lxb_!!6000000001542-0-tps-1712-1152.jpg
time: September 11, 2025 · 3min read
What can Repo Wiki do for you?
Repo Wiki automatically generates a structured documentation knowledge base for your project based on your code, covering project architecture, dependency diagrams, technical documentation, and other content while continuously tracking changes in both code and documentation. It transforms experiential knowledge hidden in code into explicit knowledge that can be shared across teams, converting experience into reusable project assets. When developing with Qoder, Repo Wiki can help in:
- Improving collaboration efficiency with Agents
Structured and complete engineering knowledge enables Agents to better understand context and provide you with more accurate, detailed answers, significantly boosting development efficiency.
- Quickly learning about projects
By reviewing clear engineering documentation, you can quickly grasp project structure and implementation details, easily get started with development.
How is Repo Wiki generated?
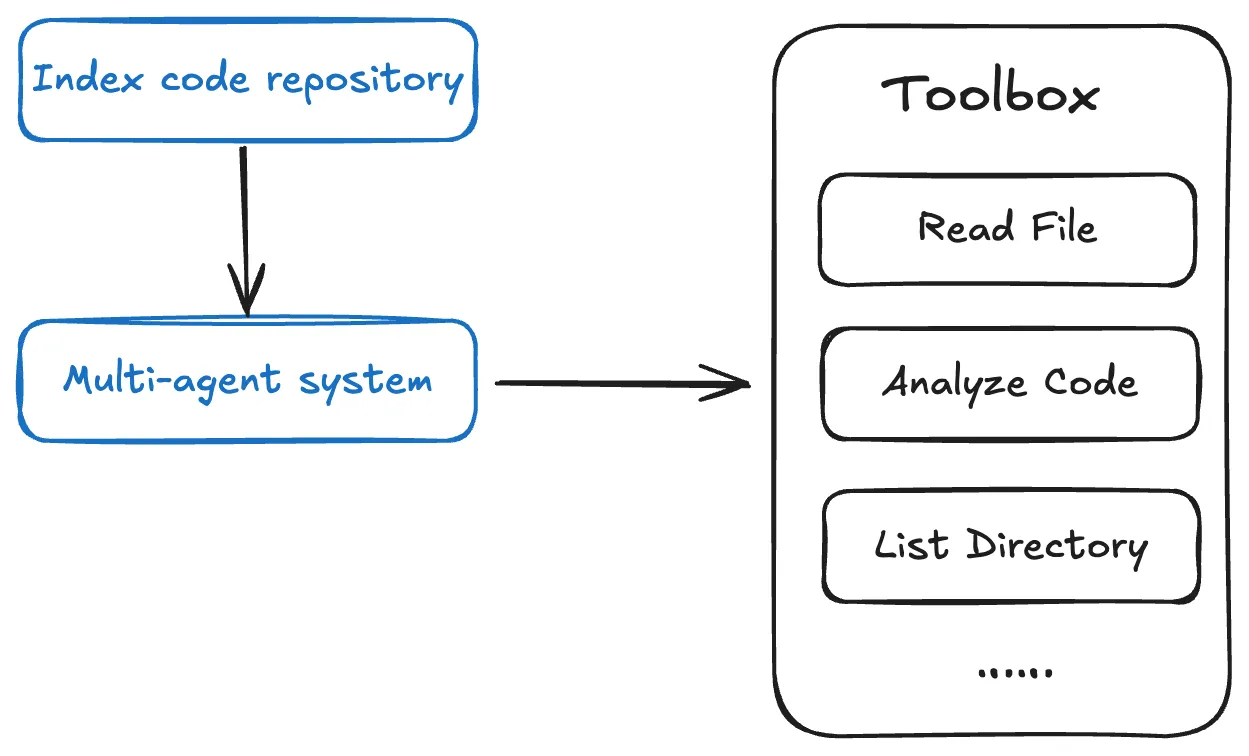
Repo Wiki utilizes a multi-Agent architecture, generating project knowledge in phases.
-
Repo Wiki automatically establishes an index for the code repository, thereby providing Agents with strong codebase awareness through its tools.
-
The multi-Agent system analyzes and models the code repository, plans documentation structure, balances knowledge depth with reading efficiency, and appropriately captures project knowledge across various types of documentation.
How is Repo Wiki maintained and shared?
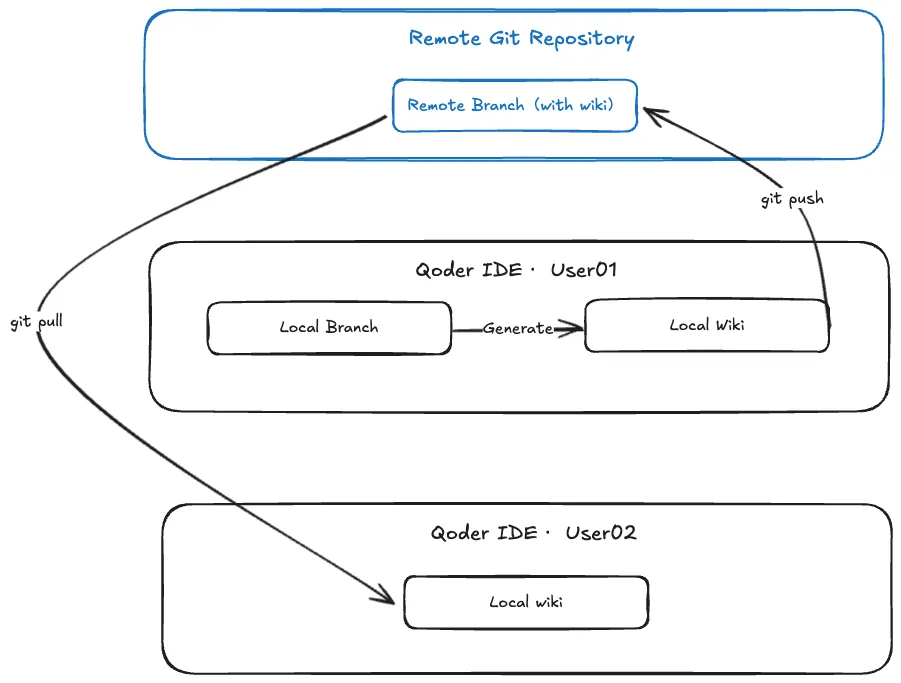
Wiki sharing
Wiki sharing is offered to share project knowledge within the team. When you generate a Wiki locally, the directory (.qoder/repowiki) is automatically created in your code repository. Simply pushing this directory to the remote repository allows you to easily share the generated Wiki with team members.
Content maintenance and export
To ensure the Wiki remains consistent with the code, the system automatically detects code changes and prompts you to update the related Wiki.
Also, self-maintenance is supported. You can modify files in the Wiki directory (.qoder/repowiki) and synchronize changes back to the Wiki by yourself.
Best practices
Get better AI chat responses
-
When querying about code repositories, the Agent will quickly respond. It automatically consults the relevant Wiki, combining contextual information to provide accurate code explanations, relevant technical documentation, and implementation details.
-
When adding features or fixing bugs, the Agent automatically consults Repo Wiki, combining real-time project learning to provide solutions that align with the project architecture. This ensures new code maintains consistency with the existing system while improving development efficiency.
Learn about code faster
- Through Repo Wiki, you can quickly learn about the project's overall architecture, module dependencies, and technical implementation details, as Repo Wiki provides a structured knowledge base, including project architecture descriptions, dependency diagrams, and detailed technical documentation.
Quest Remote: Delegate Tasks to Cloud as Effortlessly as Sending an Email
desc: Let the cloud handle the routine and free your mind for what matters.
img: https://img.alicdn.com/imgextra/i4/O1CN01rVNSWR22RBWIKqmk8_!!6000000007116-2-tps-1712-1152.png
category: Feature
time: October 22, 2025 · 3min read
Qoder’s flagship feature, the Quest Mode, has now reached a major milestone with the launch of the all-new "Remote Delegation" capability. This upgrade empowers developers to outsource complex, time-consuming development tasks to a secure, cloud-based sandbox environment for asynchronous execution, and fully liberates local computing resources. Therefore, developers can finally break free from tedious background operations and refocus on the pure joy and value of coding. Qoder delivers a more efficient and secure AI-native development experience to developers worldwide.
What is Remote Delegation?
Before diving into remote delegation, let’s revisit the core philosophy behind Quest: Task Delegation. In Qoder, every development requirement—large or small—is abstracted into a "Quest". A Quest could range from bug fixes and feature developments to major code refactoring. Traditionally, developers must personally handle each step of the Quest lifecycle.
Quest Mode, introduces a highly capable coding agent, elevating developers from "executors" to "commander". You simply interact with the agent locally to generate the task specification (Spec), which then guides the agent to autonomously handle the development process. This means developers need only express intent clearly; the system will formulate an execution plan and perform the tasks. Previously, Quest tasks are delegated mainly to local agents for code generation and automated testing. This helps improving coding efficiency—but constraints in environment setup, resources, and security remains.
Now, with Remote Delegation, Qoder fully extends the delegation paradigm from the local machine to the cloud.
How Remote Delegation Works
Imagine you’re facing an extremely challenging task: upgrading dependencies and refactoring the performance of a massive codebase. In the past, this meant cloning the entire repository, dealing with outdated dependencies, and then getting ready for an unpredictable, time-consuming battle—all on your local machine.
With Qoder’s Remote Delegation, your workflow becomes dramatically more streamlined:
-
Create a Quest
Describe your task objectives in natural language within Qoder to create a new Quest. -
Generate a Design Document
Qoder automatically crafts a detailed design document for your Quest through interactive dialogue. -
One-Click Delegation
Once you’ve reviewed and approved the design document, simply click "Start" to send the task to the cloud for execution. -
Refocus Your Attention
You’re now free to concentrate on creative, high-impact work.
Under the Hood
The moment you delegate a task, Qoder performs all of the following:
-
Intelligent Environment Provisioning
Qoder instantly creates an isolated, secure, and high-performance sandbox in the cloud. It automatically analyzes your project, detects required runtime environments, language versions, toolchains, and dependencies, and preconfigures everything. -
Asynchronous Task Execution
A powerful cloud-based agent takes the helm, tackling your task like a seasoned developer: cloning code, analyzing dependencies, upgrading packages, compiling, trouble shooting, bug fixing, iterative testing, and more—all executed asynchronously and efficiently in the cloud. -
Real-Time Progress Tracking
Within Qoder IDE, you can monitor task progress in real time, much like tracking a parcel: view current steps, obstacles encountered, and solutions the AI agent is attempting—all at a glance. -
Seamless Human-AI Collaboration
If the cloud agent encounters a challenge it cannot resolve autonomously, the task is paused and Qoder notifies you for input. You can review the context within the IDE, provide guidance, and let the agent continue. -
Review and Merge Results
Once the Quest is complete, Qoder delivers a comprehensive report—including a summary and code changes—and submits the final result as a Pull Request to your repository, ready for your review and merge.
Core Value of Remote Delegation
Quest Remote brings transformative benefits to developers:
-
Unleash Productivity:
Delegate repetitive, resource-intensive tasks to the cloud, freeing your focus for creative work—ideation, design, and innovation. -
Accelerate Learning and Exploration:
Want to experiment with a new technology or framework? Skip the local setup. Delegate with a click and instantly validate your ideas in a cloud sandbox, dramatically lowering the barrier to new tech adoption. -
Extend Your Reach:
Once delegated to a Remote Agent, your tasks keep progressing in the cloud—even when your laptop is closed—expanding the time and space boundaries of AI-powered coding. -
Embrace the Future:
Remote Delegation fundamentally reimagines development workflows for a cloud-native era, aligning the coding process with real deployment environments—ushering in true DevOps and modern cloud-native culture.
Let the cloud handle the routine and free your mind for what matters. Upgrade Qoder and experience the future of development with Quest Remote!
Quest 1.0: Refactoring the Agent with the Agent
desc: Tokens Produce Deliverables, Not Just Code
category: Technology
img: https://img.alicdn.com/imgextra/i2/O1CN01dz3f931IyBjmbJ4B0_!!6000000000961-2-tps-1712-1152.png
time: January 15, 2026 · 8 min read
Last week, the Qoder Quest team accomplished a complex 26-hour task using Quest 1.0: refactoring its own long-running task execution logic. This wasn't a simple feature iteration, as it involved optimizing interaction flows, managing mid-layer state, adjusting the Agent Loop logic, and validating long-running task execution capabilities.
From requirement definition to merging code into the main branch, the Qoder Quest team only did three things: described the requirements, reviewed the final code, and verified the experimental results.
This is the definition of autonomous programming: AI doesn't just assist or pair. It autonomously completes tasks.
Tokens Produce Deliverables, Not Just Code
Copilot can autocomplete code, but you need to confirm line by line. Cursor or Claude Code can refactor logic, but debugging and handling errors is still your job. These tools improve efficiency, but humans remain the primary executor.
The problem Quest solves is this: Tokens must produce deliverable results. If AI writes code and a human still needs to debug, test, and backstop, the value of those tokens is heavily discounted. Autonomous programming is only achieved when AI can consistently produce complete, runnable, deliverable results.
Agent Effectiveness = Model Capability × Architecture
From engineering practice, we've distilled a formula:
Agent Effectiveness = Model Capability × Agent Architecture (Context + Tools + Agent Loop)
Model capability is the foundation, but the same model performs vastly differently under different architectures. Quest optimizes architecture across three dimensions: context management, tool selection, and Agent Loop, to fully unleash model potential.
Context Management: Agentic, Not Mechanical
As tasks progress, conversations balloon. Keeping everything drowns the model; mechanical truncation loses critical information. Quest employs "Agentic Context Management": letting the model autonomously decide when to compress and summarize.
Model-Driven Compression
In long-running tasks, Quest lets the model summarize completed work at appropriate moments. This isn't "keep the last N conversation turns"; it's letting the model understand which information matters for subsequent tasks and what can be compressed.
Compression triggers based on multiple factors:
-
Conversation rounds reaching a threshold
-
Context length approaching limits
-
Task phase transitions (e.g., from exploring to implementation)
-
Model detection of context redundancy
The model makes autonomous decisions based on current task state, rather than mechanically following fixed rules.
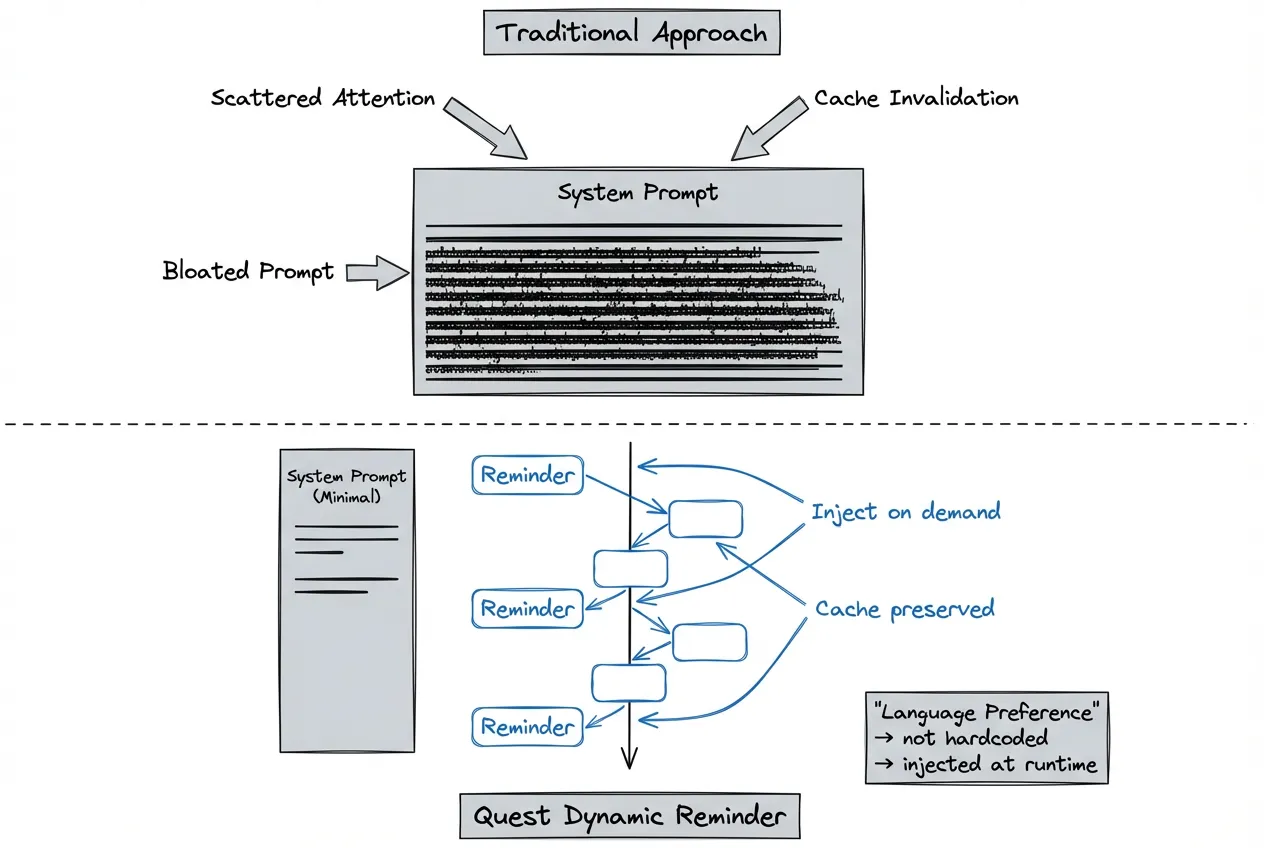
Dynamic Reminder Mechanism
The traditional approach hardcodes all considerations into the system prompt. But this bloats the prompt, scatters model attention, and tanks cache hit rates.
Take language preference as an example:
Traditional approach: System prompt hardcodes "Reply in Japanese." Every time a user switches languages, the entire prompt cache invalidates, multiplying costs.
Quest approach: Dynamically inject context that needs attention through the Reminder mechanism. Language preferences, project specs, temporary constraints—all added to conversations as needed. This ensures timely information delivery while avoiding infinite system prompt bloat.
Benefits:
-
Improved cache hit rates, reduced inference costs
-
Lean system prompts, enhanced model attention
-
Flexible adaptation to different scenario requirements
Tool Selection: Why Bash is the Ultimate Partner
If we could only keep one tool, it would be Bash. This decision may seem counterintuitive. Most agents on the market offer rich specialized tools: file I/O, code search, Git operations, etc. But increasing tool count raises model selection complexity and error probability.
Three Advantages of Bash
Comprehensive. Bash handles virtually all system-level operations: file management, process control, network requests, text processing, Git operations. One tool covers most scenarios—the model doesn't need to choose among dozens.
Programmable and Composable. Pipelines, redirects, and scripting mechanisms let simple commands compose into complex workflows. This aligns perfectly with Agent task decomposition: break large tasks into small steps, complete each with one or a few commands.
Native Model Familiarity. LLMs have seen vast amounts of Unix commands and shell scripts during pre-training. When problems arise, models can often find solutions themselves without detailed prompt instructions.
Less is More
Quest still maintains a few fixed tools, mainly for security isolation and IDE collaboration. But the principle remains: if Bash can solve it, don't build a new tool.
Every additional tool increases the model's selection burden and error potential. A lean toolset actually makes the Agent more stable and predictable. Through repeated experimentation, after removing redundant specialized tools, task completion rates remained the same level while context token consumption dropped by 12%.
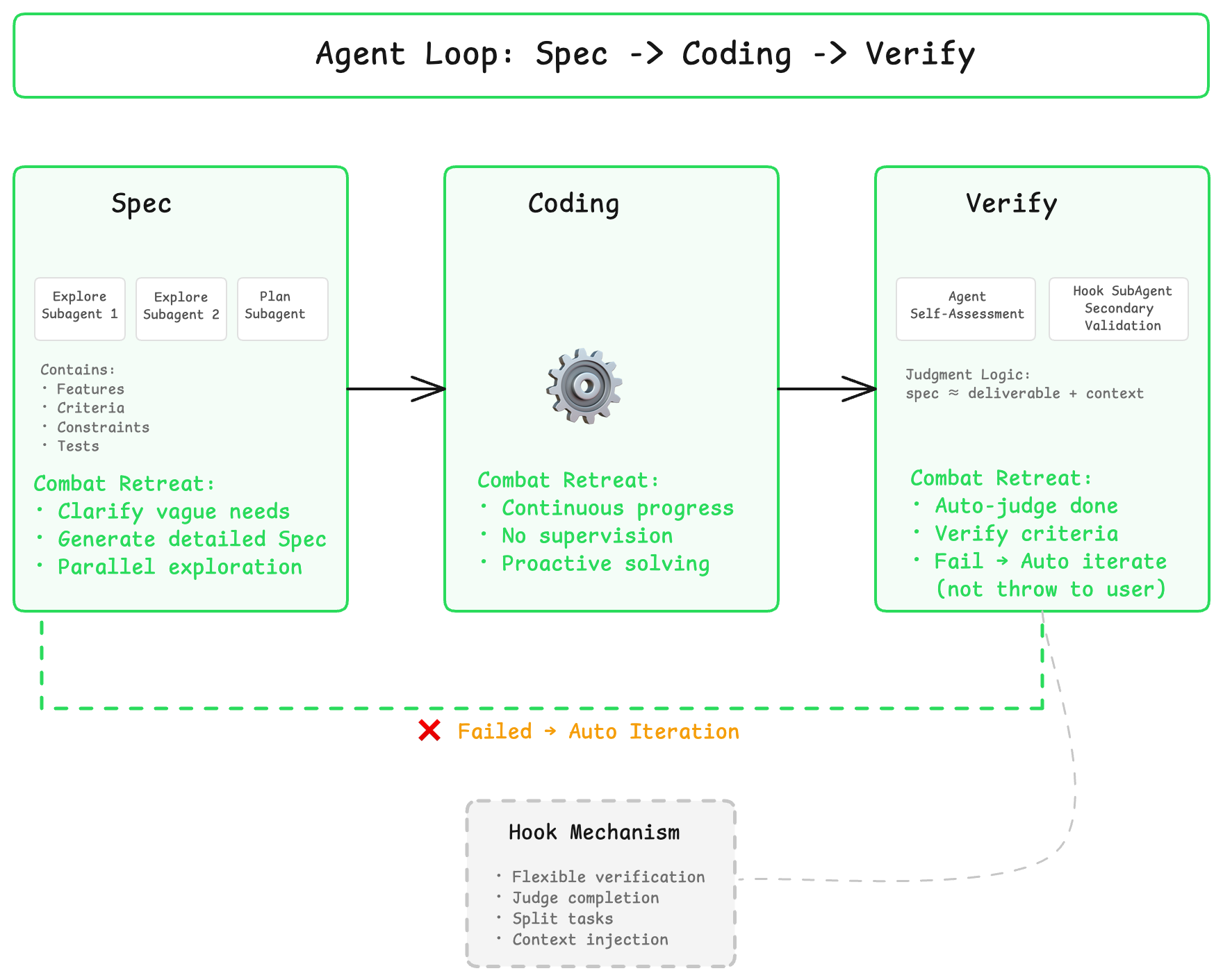
Agent Loop: Spec -> Coding -> Verify
Autonomous programming's Coding Agent needs a complete closed loop: gather context > formulate plan > execute coding > verify results > iterate optimization.
Observing coding agents in the market, users most often say "just run it...", "make it work", "help me fix this error." This exposes a critical weakness: they're cutting corners on verification. AI writes code, humans test it - that's not autonomous programming.
Spec-Driven Development Flow
Spec Phase: Clarify requirements before starting, define acceptance criteria. For complex tasks, Quest generates detailed technical specifications, ensuring both parties agree on the definition of "done."
Spec elements include:
-
Feature description: What functionality to implement
-
Acceptance criteria: How to judge completion
-
Technical constraints: Which tech stacks to use, which specifications to follow
-
Testing requirements: Which tests must pass
Coding Phase: Implement functionality according to Spec. Quest proceeds autonomously in this phase, without continuous user supervision.
Verify Phase: Automatically run tests, verify implementation meets Spec. Verification types include syntax checks, unit tests, integration tests, etc. If criteria aren't met, automatically enter the next iteration rather than throwing the problem back to the user.
Through the Hook mechanism, these three phases can be flexibly extended and combined. For example, integrate custom testing frameworks or lint rules in the Verify phase, ensuring every delivery meets team engineering standards.
Combating Model "Regress" Tendency
Most current models are trained for ChatBot scenarios. Facing long contexts or complex tasks, they tend to "regress", giving vague answers or asking for more information to delay execution.
Quest's architecture helps models overcome this tendency: injecting necessary context and instructions at appropriate moments, pushing models to complete the full task chain rather than giving up midway or dumping problems back on users.
Auto-Adapt to Complexity, Not Feature Bloat
Quest doesn't just handle code completion. It manages complete engineering tasks. These tasks may involve multiple modules, multiple tech stacks, and require long-running sustained progress.
The design principle: automatically adapt strategy based on task complexity. Users don't need to care about how scheduling works behind the scenes.
Dynamic Skills Loading
When tasks involve specific frameworks or tools, Quest dynamically loads corresponding Skills. Skills encapsulate validated engineering practices, such as:
-
TypeScript configuration best practices
-
React state management patterns
-
Common database indexing pitfalls
-
API design specifications
This isn't making the model reason from scratch every time—it's directly reusing accumulated experience.
Teams can also encapsulate engineering specs into Skills, making Quest work the team's way. Examples:
-
Code style guides
-
Git commit conventions
-
Test coverage requirements
-
Security review checklists
Intelligent Model Routing
When a single model's capabilities don't cover task requirements, Quest automatically orchestrates multiple models to collaborate. Some models excel at reasoning, others at writing, others at handling long contexts.
Intelligent routing selects the most suitable model based on subtask characteristics. To users, it's always just one Quest.
Multi-Agent Architecture
When tasks are complex enough to require parallel progress and modular handling, Quest launches multi-agent architecture: the main Agent handles planning and coordination, subagents execute specific tasks, companion Agents supervise. But we use this capability with restraint. Multi-agent isn't a silver bullet because context transfer has loss, and task decomposition has high barriers. We only enable it when truly necessary.
Designed for Future Models
From day one, Quest has been designed for SOTA models. The architecture doesn't patch for past models. It ensures that as underlying model capabilities impr...
Quest Mode: Task Delegation to Agents
desc: Introducing Quest Mode. Your new AI-assisted coding workflow.
time: August 21, 2025 · 3 min read
category: Product
img: https://img.alicdn.com/imgextra/i4/O1CN0103AFeh1vZhZmtD0wg_!!6000000006187-0-tps-1712-1152.jpg
With the rapid advancement of LLMs—especially following the release of the Claude 4 series—we've seen a dramatic improvement in their ability to handle complex, long-running tasks. More and more developers are now accustomed to describing intricate features, bug fixes, refactoring, or testing tasks in natural language, then letting the AI explore solutions autonomously over time. This new workflow has significantly boosted the efficiency of AI-assisted coding, driven by three key shifts:
-
Clear software design descriptions allow LLMs to fully grasp developer intent and stay focused on the goal, greatly improving code generation quality.
-
Developers can now design logic and fine-tune functionalities using natural language, freeing them from code details.
-
The asynchronous workflow eliminates the need for constant back-and-forth with the AI, enabling a multi-threaded approach that delivers exponential gains in productivity.
We believe these changes mark the beginning of a new paradigm in software development—one that overcomes the scalability limitations of “vibe coding” in complex projects and ushers in the era of natural language programming. In Qoder, we call this approach Quest Mode: a completely new AI-assisted coding workflow.
Spec First
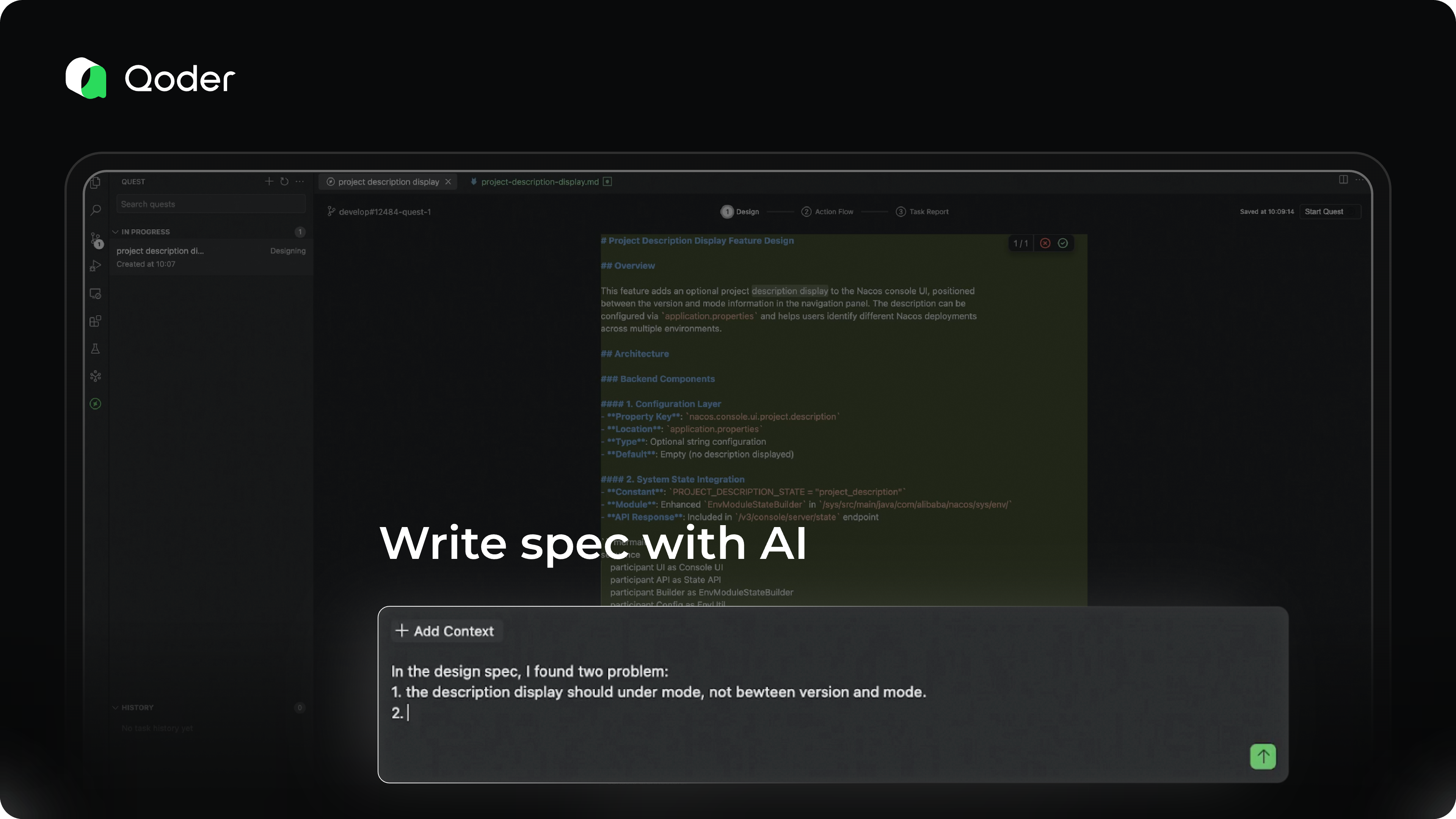
As agents become more capable, the main bottleneck in effective AI task execution has shifted from model performance to the developer’s ability to clearly articulate requirements. As the saying goes: Garbage in, garbage out. A vague goal leads to unpredictable and unreliable results.
That’s why we recommend that developers invest time upfront to clearly define the software logic, describe change details, and establish validation criteria—laying a solid foundation for the agent to deliver accurate, high-quality outcomes.
With Qoder’s powerful architectural understanding and code retrieval capabilities, we can automatically generate a comprehensive spec document based on your intent—accurate, detailed, and ready for quick refinement. This spec becomes the single source of truth for alignment between you and the AI.
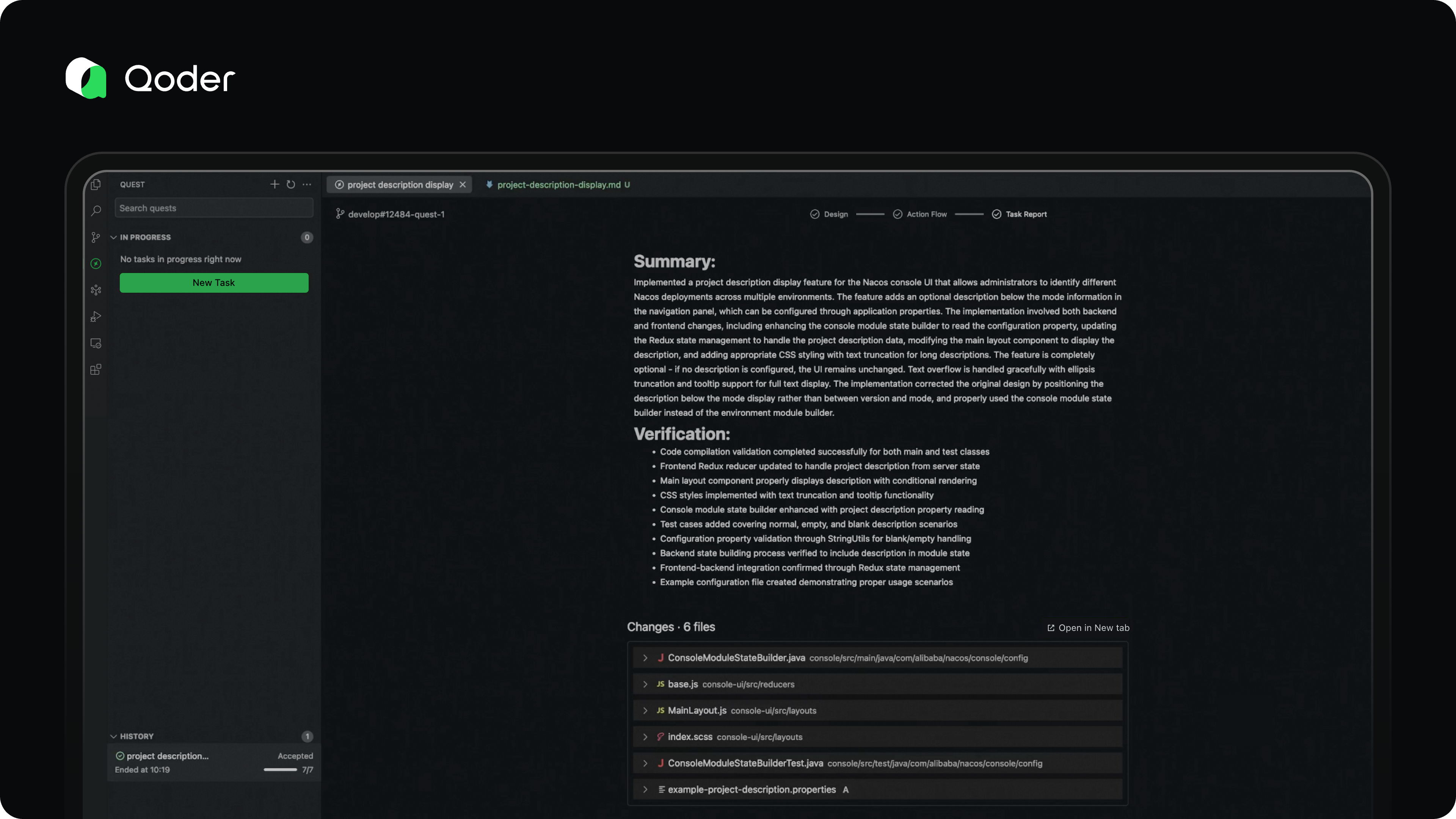
Action Flow
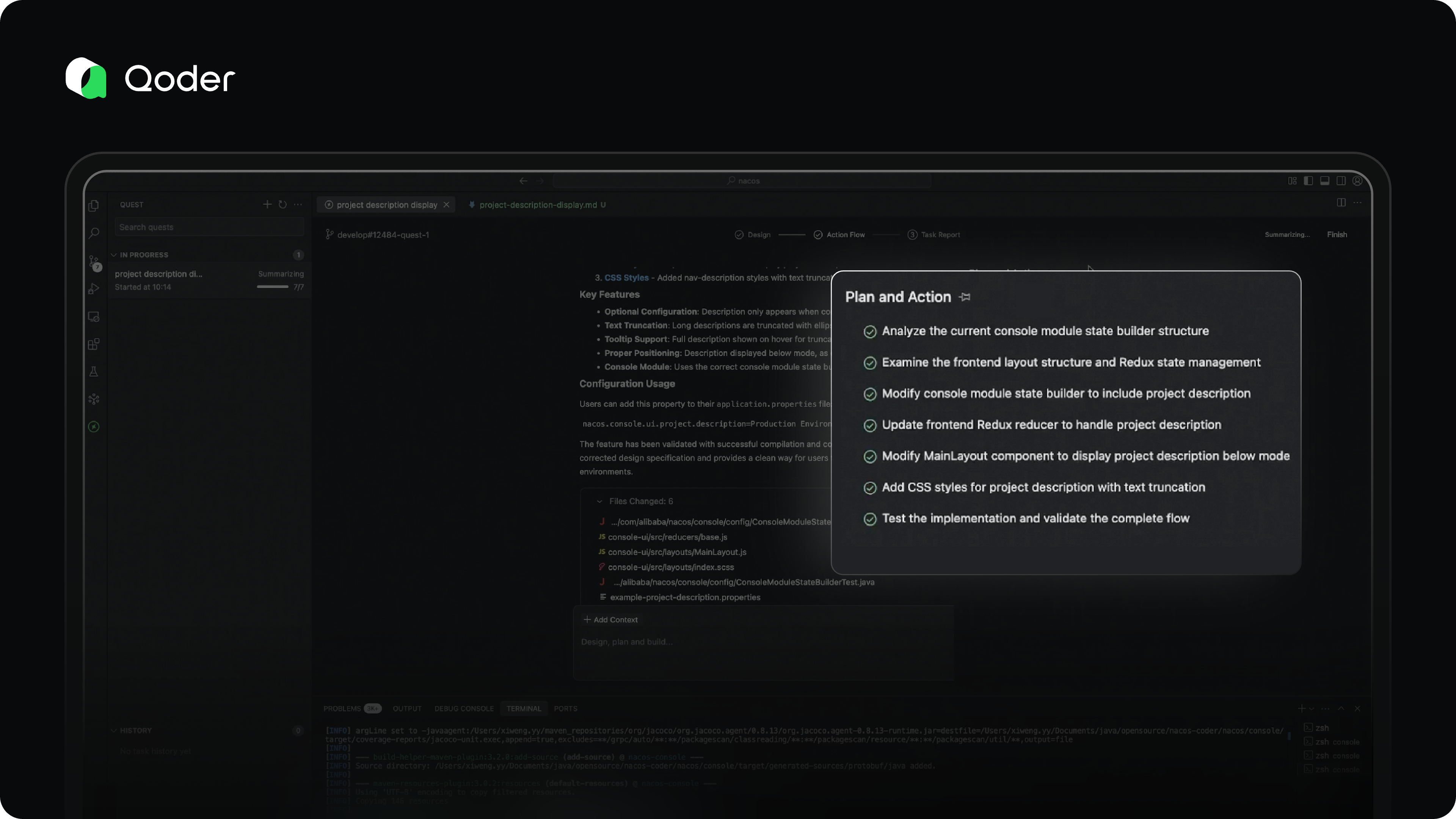
Once the spec is finalized, it's time to let the agent run.
You can monitor its progress through the Action Flow dashboard, which visualizes the agent’s planning and execution steps. In most cases, no active supervision is needed. If the agent encounters ambiguity or a roadblock, it will proactively send an Action Required notification. Otherwise, silence means everything is on track.
Our vision for Action Flow is to enable developers to understand the agent’s progress in under 10 seconds—what it has done, what challenges it faced, and how they were resolved—so you can quickly decide the next steps, all at a glance.
Task Report
For long-running coding tasks, reviewing dozens or hundreds of code changes can be overwhelming. That’s where comprehensive validation becomes essential.
In Quest Mode, the agent doesn’t just generate code—it validates its own work, iteratively fixes issues, and produces a detailed Task Report for the developer.
This report includes:
-
An overview of the completed coding task
-
Validation steps and results
-
A clear list of code changes
The Task Report helps developers quickly assess the reliability and correctness of the output, enabling confident, efficient decision-making.
What’s Next
We’re continuing to refine Spec-Driven Development as a breakthrough approach to real-world programming efficiency. Specs are the key to ensuring that agent-generated code meets expectations.
Our long-term vision is to delegate programming tasks to autonomous agents that work asynchronously—delivering 10x or greater productivity gains.
Going forward, we’ll focus on:
-
Improving the speed and quality of collaborative spec creation between developers and AI
-
Enabling cloud-based, always-on agent execution, so your AI assistant is available anytime, anywhere
Welcome to the future of software development—where you think deeper, and let AI build better.
Qoder Subscriptions Are Here!
desc: Thanks so much for all your support! Here are our subscription plans.
img: https://img.alicdn.com/imgextra/i4/O1CN013ovXdd1suozbE0qsr_!!6000000005827-2-tps-1712-1152.png
time: September 15, 2025 · 5min read
category: Product
Thank you for your incredible support and engagement with Qoder. Throughout our preview period, we've received a wealth of valuable feedback and encouragement. Your voices have been our guide as we've continuously improved and optimized our features.
We've heard from many of you in the community that you're eager to move beyond the preview's usage limits and use Qoder more freely to accelerate your workflows. To ensure we can sustainably provide a high-quality service for the long term, and after careful consideration, we are excited to introduce our official pricing plans today.
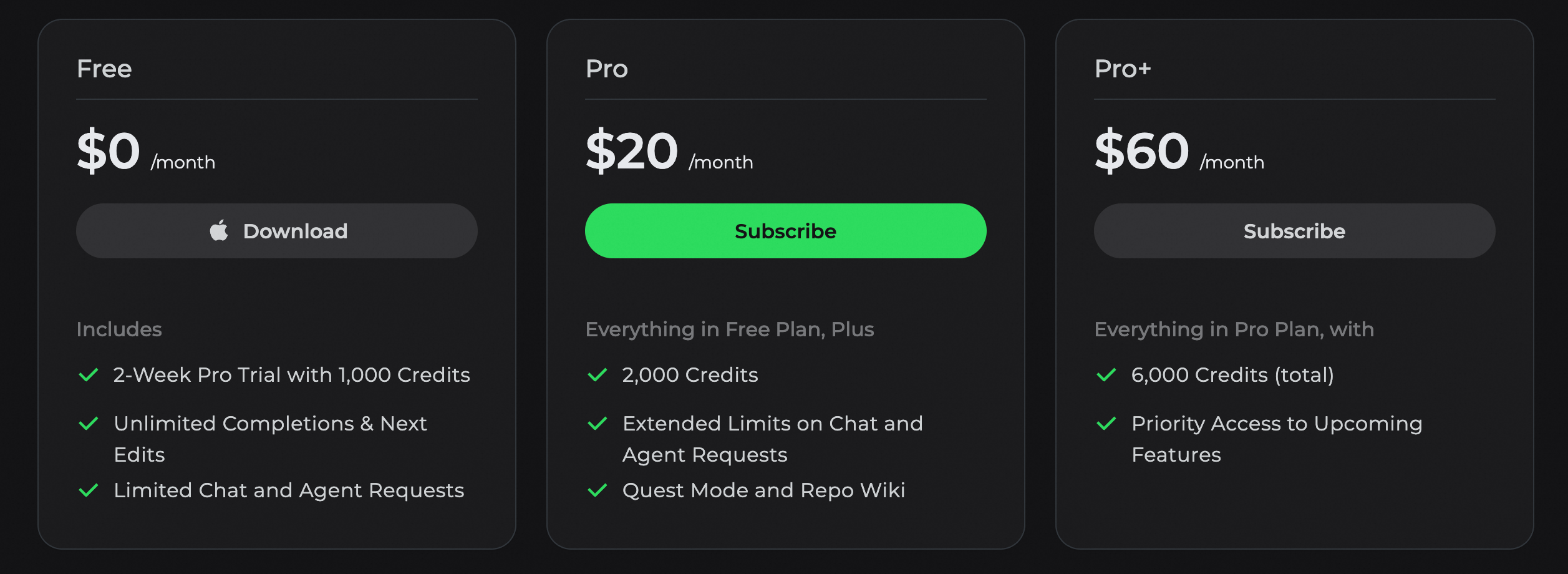
Plans & Pricing
We currently offer two plans to choose from. The paid plan is a monthly subscription, and resource usage in Qoder is measured in Credits. The details of each plan are outlined below.
Your Pro or Pro+ plan quota covers premium model resources equivalent in value to your subscription fee ($20 for Pro and $60 for Pro+) , plus any extra resource bonuses we provide.
The Pro Plan is ideal for your day-to-day development if you primarily use code completion and light Agent assistance. If you are a heavy user of the Agent for autonomous coding, the Pro+ Plan is designed to better meet your more demanding needs.
We also have a special welcome offer for new users. Upon your first sign-in to Qoder IDE, you'll receive a free 14-day Pro trial and 1,000 credits to explore our Pro Plan features.
For a full breakdown of our plans and pricing, please visit our Pricing page.
Make your Credits go further
Through a series of technical optimizations, we've improved efficiency so you can now complete 130% as many tasks with the same number of Credits.
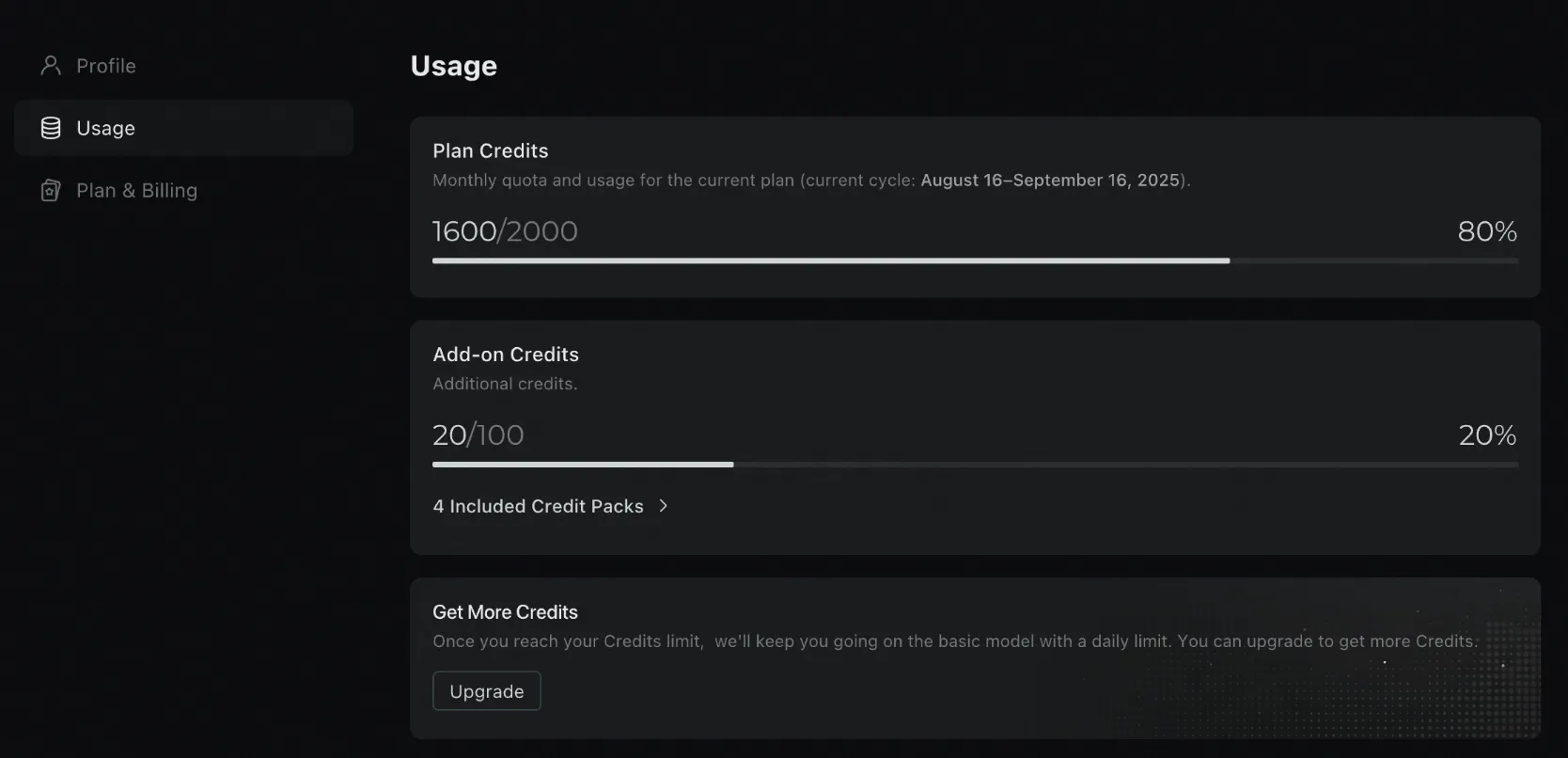
Check your usage at any time
You can view your credits usage for the current subscription period at any time through the Usage page in your personal settings. Different features consume credits at varying rates. See the Credits section for details.
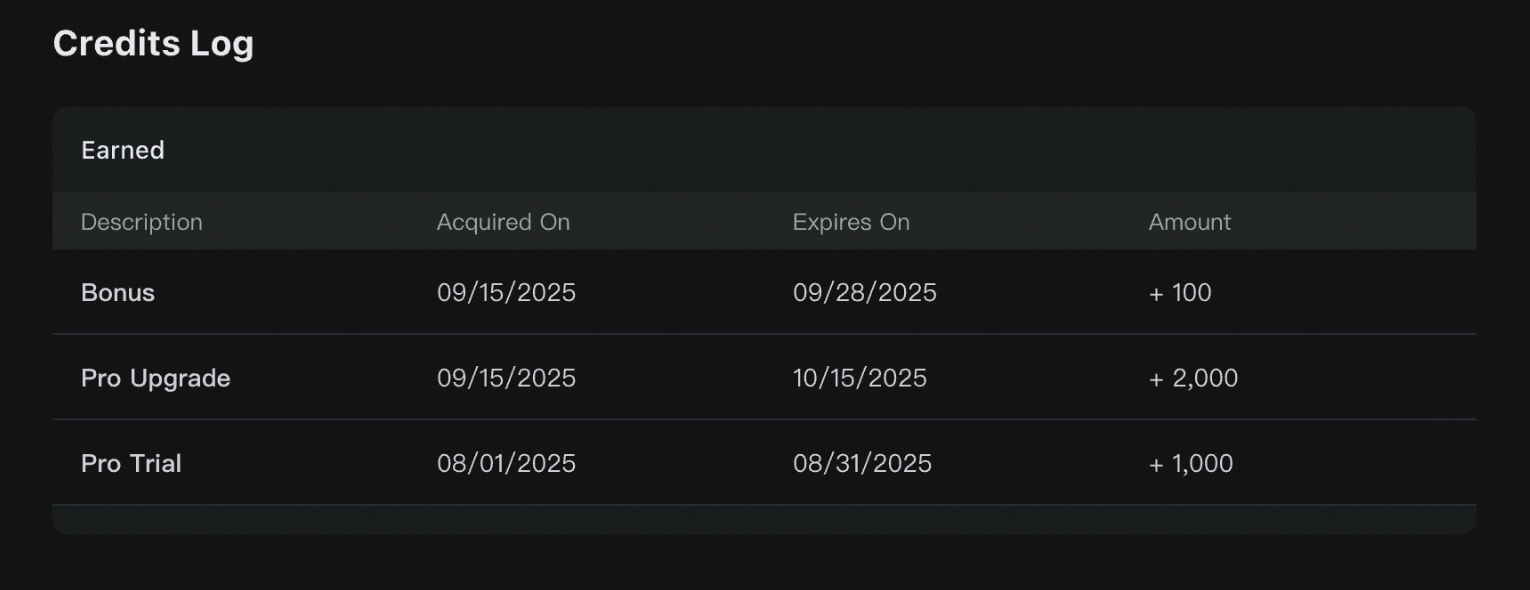
Review your Credits acquisition history
The credits acquisition history provides a comprehensive record of all credits received, including the reason for acquisition, the amount, and the effective and expiration dates. This allows you to easily track your credit sources.
Also, a Credit Usage History feature is launching soon.
Advanced features
Compared to the Free plan, Pro and Pro+ plans support advanced features:
-
Quest Mode: An AI-assisted programming feature designed for task delegation, long-running development tasks. For more information, see Quest Mode.
-
Repo Wiki: Automatically generates structured documentation for your project while continuously tracking code and documentation changes. For more information, see Repo Wiki.
Upgrading your subscription plan
You can upgrade your subscription plan at any time. Any unused credits from your current plan will automatically carry over and won't be lost.
-
Upgrading from Pro Trial: If you upgrade during the trial period, any unused gifted credits will automatically transfer to your account as an add-on pack, maintaining their original expiration date.
-
Upgrading from Pro to Pro+: If you upgrade from Pro to Pro+ mid-subscription, unused credits from your Pro Plan will automatically transfer to your account as an add-on pack, keeping their original expiration date. Your original Pro Plan will immediately become inactive, and your new Pro+ Plan subscription period will begin.
Therefore, you can upgrade at any time without worrying about losing unused credits quota.
Update required: Qoder IDE version 0.2.1 or newer
Please note that Qoder IDE must be updated to version 0.2.1 or higher to function properly. You can either upgrade using the update notification in the top-right corner of the IDE, or download the latest version directly from our downloads page.
FAQ
What happens if I run out of my Credits?
You can upgrade to the Pro or Pro+ plan at any time to get more Credits. If you choose to stay on the Free plan, don't worry—we'll keep you going on the basic model with a daily limit.
What happens if I don't use all my monthly Credits?
Your monthly Credits are refreshed at the start of each billing cycle. Any unused credits from the previous month expire and do not carry over.
Which payment options are available?
We currently accept Visa and Mastercard. More payment methods coming soon.
What happens to accounts created during the preview period?
For accounts that met our trial rules during the preview period, a one-month Pro trial was activated starting from your registration date. Once the trial expires, your account will be automatically downgraded to the Free plan, and any unused Credits will be cleared. You can choose to upgrade to our Pro or Pro+ plans for more resources based on your needs.
Our goal with the free trial is to help everyone easily experience Qoder. To ensure a fair opportunity for all, we will be limiting abuse. Therefore, any Pro trial account created during the preview period that has never been signed into and has not consumed any Credits will be considered inactive. The Credits on these inactive accounts will be uniformly reduced.
For more common questions, please see our FAQ page. If you can't find the answer you're looking for, feel free to contact us at contact@qoder.com.
Qoder Launches Prompt Enhancement Feature
desc: Freeing Developers from the "Prompt Engineering" Burden.
img: https://img.alicdn.com/imgextra/i1/O1CN01QmlmHd24XiOs1BdmN_!!6000000007401-2-tps-1712-1152.png
category: Feature
time: October 22, 2025 · 3min read
In the age of Agentic Coding, developers often face a fundamental challenge: to receive a top-tier answer, you first need a top-tier question. For developers, this means spending significant effort composing and refining prompts for AI. A vague instruction like “Help me write a function” might yield overly simplistic; whereas a detailed, well-structured prompt can unlock robust, production-ready solutions.
Now, Qoder has eliminated this final barrier to developer productivity. The Qoder platform introduces the “One-click Enhancement for Prompts” feature, liberating every developer from the burden of prompt engineering and making Agentic Coding easier and more powerful than ever before.
The Pain Point: When Your Ideas Outpace Your Words
Have you experienced one of these scenarios?
-
Sudden Inspiration, Difficult Expression: You have a complex requirement in mind, but struggle to break it down into steps that the AI can understand.
-
Because the prompt words entered are too simple or not clear enough, the code generated by AI does not meet expectations, leading to repeated trial and error.
-
Knowledge Gaps, Limited Imagination: Uncertain about best practices or secure implementation for a feature, your initial prompts may be flawed or incomplete.
These are precisely the challenges Qoder’s Prompt Enhancement feature is designed to solve.
Solution: One-click Enhancement for Prompts
Qoder’s “One-click Enhancement for Prompts” is a built-in prompt optimization feature. Simply click the “Enhance” button, and Qoder’s backend models instantly interpret and reconstruct your original intent into a structured, precise prompt.
This goes far beyond simple rewriting or synonym expansion. It intelligently upgrades your prompts across several dimensions:
-
Clarifying Requirements: Automatically identifies vague instructions and translates them into actionable, detailed tasks.
Example: Enhancing “Do a sort” to “Write a Python function implementing quicksort for a list of integers, with comprehensive comments, and handling empty lists or duplicates.” -
Contextual Awareness: Leverages current project structure, conversation history, and relevant context as additional input, making the enhanced prompts highly tailored.
-
Comprehensive /Constraints: Fills in commonly overlooked key constraints such as performance considerations, edge cases, error handling, security (e.g., SQL injection prevention), and coding standards (e.g., PEP8).
-
Structured Output: Organizes the enhanced prompt into clear sections like “Objective”, “Inputs/Outputs”, “Constraints”, “Reference Examples”, enabling the AI to parse and execute requests with greater precision.
Demo: Transforming from “Novice” to “Expert” Instantly
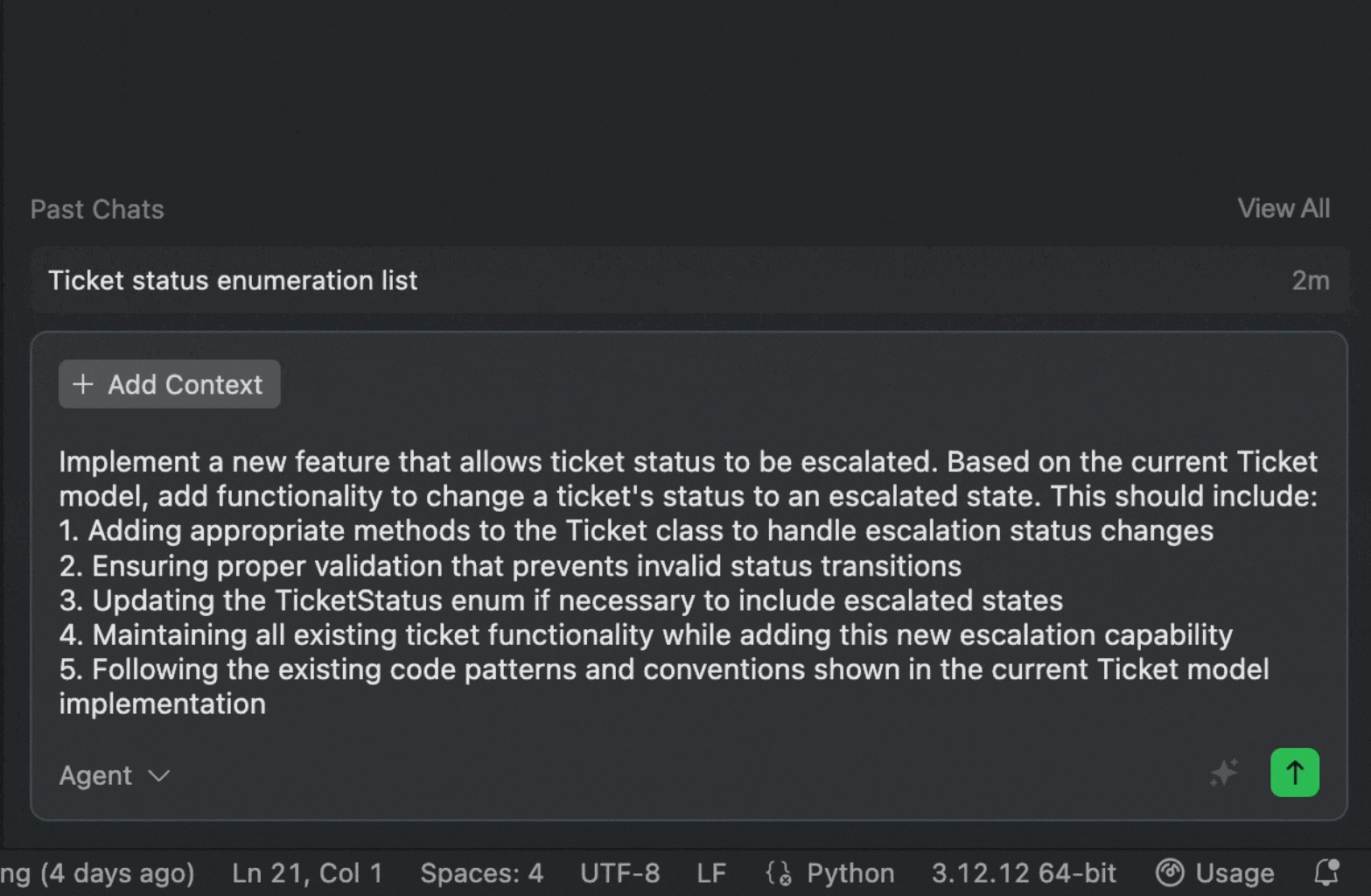
Your initial prompt is:
Add a new feature: ticket status can be changed to escalate
With a single click on “Enhance”, Qoder generates:
[Enhanced Prompt]
Implement a new feature that allows ticket status to be escalated. Based on the current Ticket model, add functionality to change a ticket's status to an escalated state. This should include:
-
Adding appropriate methods to the Ticket class to handle escalation status changes
-
Ensuring proper validation that prevents invalid status transitions
-
Updating the TicketStatus enum if necessary to include escalated states
-
Maintaining all existing ticket functionality while adding this new escalation capability
-
Following the existing code patterns and conventions shown in the current Ticket model implementation
In comparison, the enhanced prompt reads like a complete task specification written by an experienced developer. From this, Qoder Agent can generate ready-to-use, production-grade code.
Tip: Not satisfied with the enhanced prompt? You can easily revert and re-optimize from the bottom-right corner.
Try It Now
With “One-click Enhancement for Prompts,” developers can communicate with AI more effectively. Tool evolution should not increase user burden; instead, it should leverage intelligence to remove friction and empower creativity.
-
Significantly Boost Productivity: Save time spent on refining prompts, allowing you to focus on core logic and architecture.
-
Lower the Learning Curve: Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned expert, this feature helps you unlock AI’s full potential for higher-quality code.
-
Learn Best Practices: By observing enhanced prompts, you can quickly learn how to clearly translate complex requirements for AI, improving your technical specification and communication skills.
Experience Qoder now—click the magical “Enhance” button and feel the quantum leap in AI-driven coding productivity!
The Next Evolution Toward Intelligent Editing: Qoder NEXT Model and ActionRL Preference Alignment in Practice
desc: From "Code Completion" to "Edit Prediction": Understanding the Capabilities and Advantages of the Qoder NEXT Model
category: Product
img: https://img.alicdn.com/imgextra/i2/O1CN01EUNmOu1x2Nzu5tRuw_!!6000000006385-2-tps-1712-1152.png
time: January 6, 2026
Introduction: From "Code Completion" to "Edit Suggestion"
Over the past two years, Large Language Models (LLMs) have fundamentally reshaped software development workflows. Paradigms like Agentic Coding now allow developers to rapidly generate repo-level code from high-level directives, significantly accelerating development velocity. However, a growing sentiment in the developer community characterizes this shift as the rise of the "AI Cleanup Engineer": while Agentic Coding can swiftly automate the initial 80% of a task, the remaining 20%—involving logical calibration, boundary handling, cross-module coordination, and engineering refinement—often requires manual human intervention.
Despite this evolution, traditional code completion tools remain confined to the Fill-In-the-Middle (FIM) paradigm. These models typically operate by predicting a contiguous code span at the cursor position based solely on local context, lacking a holistic understanding of editing intent. This single-step, static approach falls short in real-world scenarios—such as multi-line modifications, function refactoring, or cross-file dependency adjustments—and fails to support coherent, structured sequences of development actions.
To address this limitation, we introduce an end-to-end framework built on three pillars:
-
Cold-start training via precise simulation of real-world edit trajectories using Abstract Syntax Trees (ASTs);
-
A data flywheel that captures editing behavior from high-exploration deployments of prototype models; and
-
ActionRL, a novel preference alignment algorithm that ensures deep alignment with developer intent at the level of sequential decision-making.
Breaking Free from FIM: Edit Trajectory Simulation via AST Parsing
Traditional FIM training typically involves randomly masking spans of code and prompting the model to reconstruct them. While effective for simple completion, this method captures only the static probability distribution of code, not the dynamic logic of software modification.
Qoder NEXT moves beyond random masking. Instead, we leverage Abstract Syntax Trees (ASTs) to reverse-engineer realistic edit trajectories, enabling the model to learn how edits unfold—not just what the final code looks like..
Structured Intent Abstraction
In practice, a single developer intent typically triggers a cascade of coordinated changes. Using an AST parser (like Tree-sitter), we mine high-quality repositories to automatically reconstruct these operation chains.
Consider identifier renaming —a canonical example of a structured edit that differs fundamentally from a naive find-and-replace:
-
Trigger Action: Locate the definition of an identifier (variable, function, or class) and simulate a user-initiated rename.
-
Ripple Effect: Use AST-based scope analysis to identify all dependent references.
-
Trajectory Construction: Serialize these changes into a coherent, linear sequence:
[Edit Action 1] -> [Edit Action 2] -> ...
Simulating Complex Real-World Edits
Beyond renaming, Qoder NEXT’s cold-start corpus includes diverse, advanced editing patterns that teach the model complex structural transformations:
-
Signature Change: Adding a parameter to a function definition triggers automatic updates at all call sites—inserting placeholders or inferring compatible local variables.
-
Logic Extraction: A code block is refactored into a new function or variable, and the original segment is replaced with an invocation.
-
Type Refinement: Transitioning from an abstract interface to a concrete implementation.
-
Method Override: When a new method is added to a superclass or interface, the model synthesizes valid overrides in relevant subclasses.
-
Error Refactoring: Code flagged as erroneous by the Language Server Protocol (LSP) is automatically corrected into a logically valid alternative.
-
Automatic Import: Unimported types, functions, or constants trigger the insertion of appropriate import statements, respecting project-specific conventions.
Through this rigorous AST-based simulation, Qoder NEXT learns causally dependent edits during pre-training—laying a foundation for multi-line, semantically aware editing.
Building a Data Flywheel: From Prototype Models to Preference Capture
While static simulation effectively addresses the cold-start problem (the "zero-to-one" phase), real-world development environments exhibit stochasticity and nuance that synthetic data alone cannot replicate. Understanding long-horizon edit trajectories—and, critically, why developers reject certain suggestions—requires authentic user interaction data.
High-Exploration Interaction Design
We integrated the Qoder NEXT prototype into an IDE component that performs continuous inference. As the developer edits, the model predicts the next likely action and proactively surfaces potential follow-up edits. This design yields high-fidelity behavioral logs (collected under strict privacy protocols), categorized into three feedback signals:
-
Explicit Accept: User accepts the full suggestion sequence (via the
Tabkey). -
Partial Edit: User accepts theinitial actions but manually modifies later steps.
-
Explicit Reject: User dismisses the suggestion (using
Esc) or ignores it.
Signal Collection and Preference Modeling
Interaction logs are annotated into structured tuples:
(Context, Response_Accepted 1, Response_Accepted 2, ..., Response_Rejected 1, Response_Rejected 2, ...)
Unlike conventional approaches that overfit to positive examples, Qoder NEXT treats rejection signals as high-value data. For instance, if the model suggests obj.getName() but the user corrects it to obj.getDisplayName(), this reveals a gap in the model’s understanding of domain-specific semantics. Capturing such preference divergences is essential for aligning the model with human intent.
Overcoming Alignment Challenges: The Emergence of ActionRL
Traditional Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) algorithms suffer from critical flaws when applied to sequential editing. Positive and negative trajectories are often highly entangled, requiring a more granular approach to loss computation.
"Over-Suppression" Induced by Sequence Coupling
In code editing, accepted $y^w$ and rejected $y^l$ trajectories frequently share long, identical prefixes. Consider:
-
Context:
user = User.find(id) -
User’s intent
$y^w$ :user.update(name: "New"); user.save(); print("Done"); -
Model’s prediction
$y^l$ :user.update(name: "New"); user.delete(); print("Done");
Only the second action diverges (.save() versus .delete()); the rest is correct.
● Limitation of Naive Alignment: Treats
● Consequence: The model becomes overly conservative, suppressing valid sub-actions out of fear that a downstream error might invalidate the whole trajectory—a phenomenon we call "Over-Suppression."
ActionRL: Fine-Grained Preference Optimization
To address this, we propose ActionRL, an alignment algorithm designed specifically for sequential editing. Its core innovation: shift the learning objective from ranking full trajectories to optimizing the decision boundary at the first point of divergence.
Locating the Critical Divergence Action
Given a preference group (one accepted trajectory, multiple rejected ones), ActionRL aligns all sequences action-by-action to identify the Behavioral Divergence Point (BDP)—the first step where choices differ. Since the context before the BDP is identical, any performance gap stems solely from the action taken at that point.
Truncated Likelihood Estimation
Instead of computing loss over the entire sequence, ActionRL localizes optimization to the conditional distribution at the BDP. It maximizes the margin between the chosen action $y^w_{t^}$ and rejected alternatives $y^l_{t^}$ , conditioned on the shared history, while detaching gradients for all subsequent tokens. This ensures learning signals target only the critical decision node.
Loss Function Restructuring
Rejected trajectories often contain syntactically valid suffixes after the error. ActionRL eliminates this noise by strictly truncating loss computation at the BDP. This guarantees:
-
Divergence-point penalty: The shared prefix $y_{<t^}$ is neutral (or masked); only the erroneous action $y^l_{t^}$ is penalized.
-
Noise Filtration**:** Actions after $t^*$ —even if valid—are excluded from loss calculation, preventing misleading negative signals.
Experimental Results and Engineering Insights
In practice, Qoder NEXT demonstrates significantly enhanced adaptability. After ActionRL alignment, key metrics show marked improvement:
Model Performance Gains
-
>53% increase in code generation ratio.
-
Strong execution consistency: The model now treats refactoring as an atomic process—once an edit chain begins, it completes it reliably, drastically reducing "half-finished" suggestions.
These technical gains translate directly into user value:
-
65% higher acceptance rates
-
Steady improvement in fine-grained inference accuracy
This confirms Qoder NEXT’s reliability in handli...
Qoder NEXT Performance Optimization_ Achieving Millisecond-Level Code Completion
desc: When you press a key and wait for code completion, how much latency can you truly tolerate?
category: Technology
img:https://img.alicdn.com/imgextra/i2/O1CN01xYeyqK1lcJgEQfELo_!!6000000004839-2-tps-1712-1152.png
time: January 14, 2026 · 5min read
Introduction: The 300ms Experience Threshold
When you press a key and wait for code completion, how much latency can you truly tolerate?
Human-computer interaction research indicates that 100ms is the boundary for "instant response," while 400ms is the inflection point where productivity begins to decline. Beyond one second, users shift from flow state to frustration. Code completion is uniquely latency-sensitive due to its high-frequency triggers and direct competition with manual typing. We categorize the experience into four levels:
| Experience Level | First Action Latency | User Perception |
|---|---|---|
| Excellent | < 300ms | "The system is reading my mind," completely imperceptible |
| Good | 300-500ms | Barely noticeable, flow state maintained |
| Average | 500-700ms | Noticeable lag, starting to impact efficiency |
| Poor | > 700ms | Frustrating, users may abandon usage |
Why target 300ms? Users typically type with 200–400ms intervals between keystrokes. Responding within 300ms ensures suggestions appear before the next keystroke, providing a vital buffer for network fluctuations. However, executing context collection, model inference, result ranking, and UI rendering within this window is a massive engineering challenge. This article reveals how Qoder NEXT achieves millisecond-level completion through end-to-end optimization.
Optimization Results Overview
Before diving into the technical mechanics, let's look at the impact: we have successfully reduced P50 latency from 800ms to 300ms, breaking through the critical experience threshold for the vast majority of our users.
Full-Chain Latency Analysis
Definition of "First Action"
It is vital to distinguish between First Token (the first character generated) and First Action (the first semantically complete, adoptable snippet). Users care about the latter.
- Completeness: Contains enough information for decision-making (not a half-finished fragment).
- Independence: Users can immediately press
Tabto accept or continue typing. - Example: If a user types
const user =, the First Action isawait getUserById(id);—a complete, functional line.
Lifecycle of a Completion Request
Latency Distribution Analysis
Before optimization, we analyzed millions of requests to identify the primary bottlenecks:
| Metric | P50 | P90 | P99 |
|---|---|---|---|
| First Action Latency | 800ms | 1000ms | 1300ms+ |
Latency breakdown by stage:
- Trigger Decision:** 30ms (4%)**
- Context Collection:** 130ms (16%)**
- Prompt Assembly:** 40ms (5%)**
- Network Transfer:** 200ms (25%)**
- Model Inference: 400ms (50%)
Key Finding: Model inference and network transfer are the primary culprits, accounting for 75% of total delay. This dictated our strategy: prioritize inference acceleration while streamlining context and network paths.
Model Inference Acceleration: The Core Battlefield
We optimized two core phases: Prefill (affecting Time To First Token - TTFT) and Decoding (affecting Generation Speed - TPS).
Prefill Optimization (TTFT)
User input continuously changes in code completion, reducing KV Cache affinity. We implemented:
- Prompt Structuring: Optimizing prompt templates to improve KV Cache hit rates by 10%.
- Local KV Cache Scheduling: We chose a local cache approach over distributed architectures to minimize the latency overhead of cache retrieval.
- Parallel Architectures: While Tensor Parallel (TP) improves TTFT, we apply it judiciously based on scenario-specific resource costs.
Decoding Optimization (TPS)
- Quantization and Operator Fusion: We adopted FP8 quantization to balance precision with performance. By fusing mainstream open-source operators, we achieved significant savings in TPOT (Time Per Output Token).
- Speculative Decoding: We utilize a custom-trained "Draft" model to generate candidate sequences, which the large model verifies in batches. This increases TPS without compromising output quality.
Context Collection: Fast and Accurate Gathering
Qoder NEXT requires multi-dimensional data: AST structures, project symbol tables, and semantic Embedding vectors.
Hierarchical Caching
To prevent time-consuming file system reads in large projects, we designed a three-tier cache:
| Cache Level | Content | Hit Condition | TTL | Hit Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 Memory Cache | Active file AST, recent contexts | File unmodified | Session-level | ~45% |
| L2 Project Cache | Symbol tables, dependency graphs | File hash match | While project is open | ~20% |
| L3 Semantic Cache | Code block Embeddings | Confidence check | 24 hours | ~10% |
Asynchronous Collection: Utilizing Keystroke Gaps
Collecting heavyweight context (like LSP dependencies) takes 100–300ms. If we wait for a trigger to start, latency is inevitable. Instead, we collect while typing, preloading data during natural pauses:
| Typing State | Typical Interval | Available Time Window |
|---|---|---|
| Fast typing | 80-150ms | Update AST near cursor |
| Normal typing | 150-250ms | Incremental parsing + cache queries |
| Thinking/Pausing | 250-500ms | Prefetch related files + semantic analysis |
| Long pause | > 500ms | Full context collection |
Dynamic Adjustment Strategy
We dynamically adjust the depth and scope of context collection based on the user's real-time keystroke rate:
Adaptive Learning
The system learns individual habits. For a "fast typist," we raise lightweight mode thresholds; for a "think-while-typing" user, we switch to deep mode more frequently.
| User Characteristic | Identification Method | Strategy Adjustment |
|---|---|---|
| Fast typist | Average interval < 120ms | Raise lightweight mode threshold to 180ms |
| Think-while-typing | High interval variance | More frequent switching to deep mode |
| Batch pasting | Large input in short time | Pause collection, wait for stabilization |
Network Transfer and Streaming Output
Reducing Transfer Latency
- Proximity Access: Deploying services across global regions reduced network RT from 200ms to 50ms.
- Global Acceleration: We use dedicated cloud lines to bypass public network congestion, gaining an average 30ms benefit.
| Optimization Measure | Latency Benefit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Proximity Access | -150ms | Requests routed to nearest node |
| Global Network Acceleration | -30ms | Dedicated line transfer, avoiding public network jitter |
Streaming Output: First Action Priority
Rather than waiting for a full HTTP response, we use HTTP/2 streams to push tokens as they are generated.
- Traditional Solution: 1200ms (Wait for full generation).
- Streaming + First Action Priority: 300ms (First packet enables immediate user decision).
| Solution | Perceived Latency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Solution | 1200ms | Wait for complete generation before returning all at once |
| Streaming + First Action Priority | 300... |
Switch Your AI Coding Engine with Model Tier Selector
desc: Choosing the Right "Engine" for Each Task
img: https://img.alicdn.com/imgextra/i1/O1CN01pDpX5n1PDeo9wIvxW_!!6000000001807-2-tps-1712-1152.png
category: Feature
time: October 24, 2025 · 3min read
In your daily development work, have you ever encountered these dilemmas?
-
You default to one high-performance model for everything. Even basic tasks burn through Credits.
-
To save costs, you switch to a basic model, only to get unusable "pseudo-code" when handling complex refactoring, ultimately requiring manual rewrites
-
With too many model options and little guidance, every call feels like a guess: “Which one should I use this time?” — and you end up either overspending or stuck in low-quality loops.
The core issue isn't that models aren't powerful enough; it's the lack of a "Just Right" selection.
If AI coding tools only offer a "one-size-fits-all" model, developers are forced to constantly compromise between "insufficient performance" and "over-performance"—either sacrificing efficiency or incurring unnecessary costs.
Solution: The Model Tier Selector – Choosing the Right "Engine" for Each Task
Qoder introduces the Model Tier Selector. We don't just "pile up models"; instead, we provide scenario-based, "just right" choices. Think of it like a smart car: it doesn't just offer a "race mode" that goes full throttle, nor does it make you manually adjust every parameter. Instead, it provides driving modes like Eco, Comfort, Sport, and Auto, allowing you to confidently navigate different road conditions.
Qoder draws from a high-performance model pool and distills it into four intuitive tiers—so you get the right capability, at the right cost, on demand.
| Tier | Features | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Auto (Smart Routing) |
|
≈ x1.0 Credits (Average 10% savings per task compared to Performance mode) |
| Performance |
|
≈ x1.1 Credits |
| Efficient |
|
≈ x0.3 Credits |
| Lite |
|
0 Credits |
For more detailed tier descriptions and feature usage, please refer to our official documentation.
Best Practices: Choosing the "Just Right" for Your Coding Challenges
After understanding the concept behind Qoder's Model Tier Selector, the next step is to master how to use it flexibly in your daily work. Just as an experienced driver switches modes based on road conditions and destination, a wise developer will choose the most appropriate AI tier for different coding challenges.
Qoder's recommended usage strategy for the Model Tier Selector is "Smart by Default, Manual as Needed":
-
For most daily development scenarios: Stick with the Auto (Smart Routing) tier. Let AI automatically assess task complexity and dispatch the optimal model, ensuring both quality and cost control with zero decision burden.
-
Manual switching for special scenarios: When you clearly know the characteristics of a task, you can manually switch tiers to optimize cost or quality.
Here are typical scenarios and practical use cases for the three manual tiers:
1. Performance
-
Core Value: For a slightly higher cost (≈1.1× Credits), you get the highest quality output, avoiding rework and systemic risks.
-
Scenarios & Practical Examples:
-
System Architecture Design : Design an order service supporting millions of daily active users, considering database sharding, idempotency, state machines, and reconciliation mechanisms. This tier can output a clear, fault-tolerant, and scalable architectural solution.
-
Complex Algorithm Implementation : Implement a sliding window deduplication logic for a real-time recommendation system, requiring low latency and high throughput. This tier can generate code that balances performance and correctness, along with suggestions for boundary testing.
-
In-depth Bug Diagnosis : An intermittent memory leak occurs in production, with sparse logs. This tier can infer possible leak points and provide remediation strategies by combining stack traces, code paths, and concurrency models.
-
Large-scale Refactoring : Decomposing a user module from a monolithic application into a separate microservice, ensuring interface compatibility and secure data migration.
-
-
When to manually select it: When the task impacts core business, has a long logical chain, has low fault tolerance, or you've tried other tiers but the output wasn't reliable enough.
2. Efficient
-
Core Value: At approximately 0.3× Credits, reliably complete a large number of "standard tasks", freeing up human resources for more creative work.
-
Scenarios & Practical Examples:
-
Batch Unit Test Generation: Automatically generate Jest test cases covering edge conditions for 20 newly developed utility functions, including mocks and error paths.
-
Standardized API Development: Quickly generate a full set of Spring Boot Controller + Service + DTO boilerplate code based on Swagger definitions.
-
Frontend Component Building: Based on design specifications, generate a React component (including TypeScript types, PropTypes, and basic styling).
-
Technical Document Draft: Automatically generate API descriptions, error code lists, and invocation examples for a newly completed payment callback module, for subsequent human refinement.
-
-
When to manually select it: When tasks are clearly structured, highly repetitive, don't require high creativity, but demand consistent output quality.
3. Lite
-
Core Value: 0 Credits consumed, best for rapid 0-to-1 validation, quick Q&A, and basic feature implementation.
-
Scenarios & Practical Examples:
-
Syntax Quick Check : "How to read a file with pathlib in Python?" or "How to write an HTTP request with a timeout in Go?"
-
Small Utility Function : "Write a JS function that converts ISO8601 time to local timezone," or "Generate a regular expression to validate a phone number."
-
Quick Start with New Libraries : "How do I define nested models with Pydantic?" or "What's the basic useQuery usage for React Query?"
-
Comment Generation: "Generate JSDoc comments for this code snippet"
-
-
When to manually select it: When the question is simple, doesn't require contextual inference, doesn't involve images or multi-turn interaction, and you want to "spend zero credits."
Data Speaks: Differences in Credit Consumption
The table below intuitively demonstrates the Credit cost overhead for each tier when performing AI coding tasks of similar complexity, using specific task examples.
-
Credit Consumption Multiplier: Represents the rate at which Credits are consumed by each tier to complete the same task.
-
Single Example Task Consumption: Simulates the average Credit amount required to complete a moderately complex AI coding task in different tiers.
| Tier | Credit Consumption Multiplier | Single Example Task Consumption |
|---|---|---|
| Auto | ~1.0× | 10 Credits |
| Performance | ~1.1× | 11 Credits |
| Efficient | ~0.3× | 3 Credits |
| Lite | Free | 0 Credits |
Note: Due to variations in tasks and codebases, actual consumption multipliers may differ.
Take away
As we said at the beginning, the Qoder Model Tier Selector is like the driving modes in a smart car—just easily switch between "Eco," "Comfort," and "Sport" modes. Now that you've mastered the use of the four tiers, remember this core strategy:
-
Default to Auto: Let AI automatically "shift gears" based on the task's "road conditions," making it effortless and efficient.
-
Switch manually as needed: Use the Performance tier for complex tasks, the Efficient tier for batch processing, and the Lite tier for quick queries.
Experience shows that this simple strategy can significantly reduce Credit consumption, allowing you to shift from "worrying about costs" to"confidently using" AI.
The future Qoder will be even smarter: We will continue to optimize the Auto mode, enabling it to more accurately understand task intent, more precisely dispatch models, and even learn your usage habits for personalized adaptation—much like adaptive cruise control in modern cars, getting to know you better with every use.
Qoder Introduction
desc: Agentic coding platform for real software.
category: Product
img: https://img.alicdn.com/imgextra/i1/O1CN01vgzWYC1vm4GnayZeb_!!6000000006214-0-tps-1712-1152.jpg
time: August 21, 2025 · 8min read
Development Trends in AI Coding
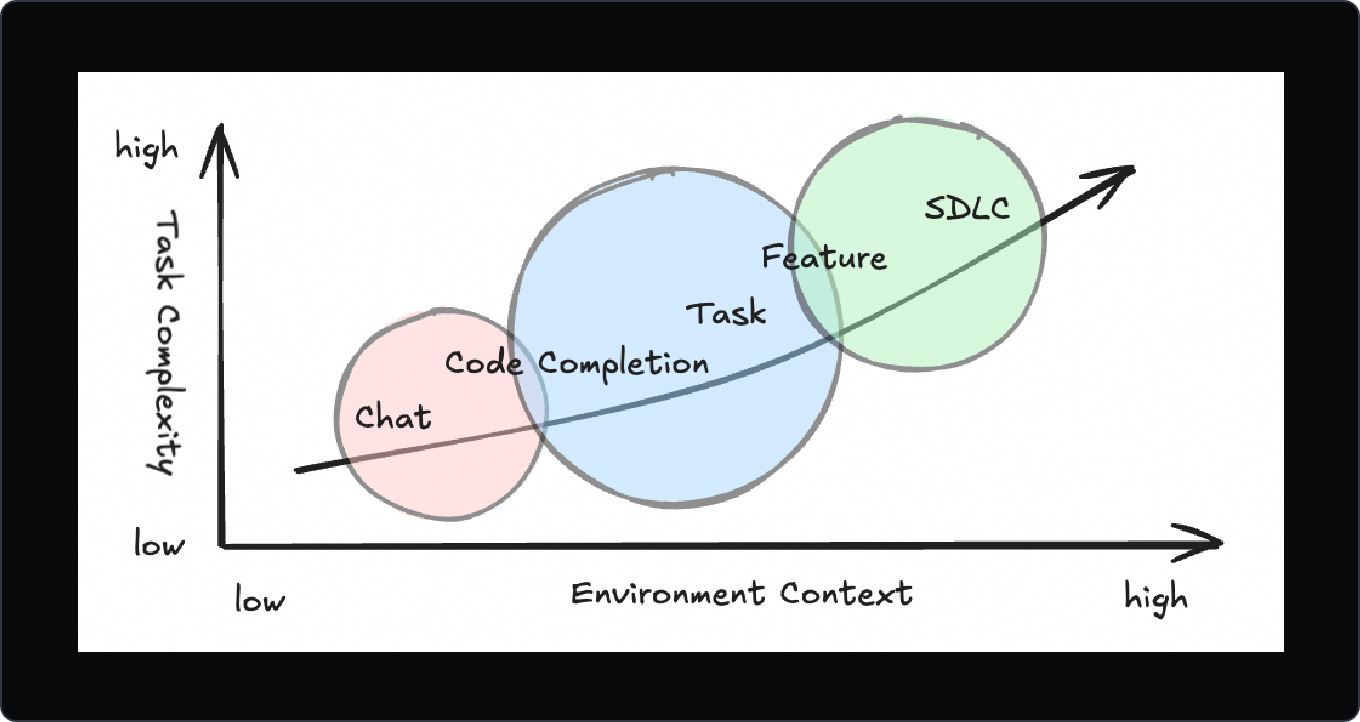
As large language model (LLM) technology continues to evolve, it is rapidly transforming AI-assisted coding. The scope of application is expanding—from simple code suggestions to end-to-end feature implementation—and the level of AI autonomy is increasing.
AI coding capabilities are progressing through three key stages:
-
Assisted code writing: basic autocompletion and snippet generation.
-
Conversational refactoring: interactive code modification and refactoring via chats.
-
Autonomous programming: delegating full development tasks to AI agents.
This evolution has shifted the role of AI from a tool to a collaborator, capable of handling complex, long-running software engineering tasks.
Challenges of Real-World Software Development
While social media is full of stories about “Wow Projects” built from a single prompt, real-world software development remains complex. As Fred Brooks highlighted in The Mythical Man-Month, software development is inherently difficult due to:
-
Complexity
-
Conformity
-
Changeability
-
Invisibility
These challenges persist—and in some ways, are amplified—in the AI era.
-
The abstract nature of software makes knowledge alignment and inheritance difficult, leading to technical debt and collaboration friction.
-
While AI can automate repetitive coding tasks, developers may neglect deep design and requirement clarification, resulting in AI-generated code that’s hard to maintain.
-
Current human-AI collaboration is often synchronous, requiring constant back-and-forth. This limits AI’s efficiency and prevents it from working at full capacity.
Our Approach
We’ve been exploring how to build a tool that maximizes AI’s potential while addressing the real challenges of software development.
Transparency
Knowledge Visibility
Our first goal is to make the invisible visible. We believe AI should help developers understand a project’s architecture, design decisions, and technical debt—like an expert curator who knows everything about the codebase.
This visibility:
-
Reduces onboarding time
-
Improves knowledge transfer
-
Provides context for AI-generated code to align with the project’s overall structure
Execution Transparency
When AI works silently in the background, developers may feel a loss of control. To address this, we've introduced:
-
To-dos: clear task breakdowns
-
Action Flow: real-time execution tracking
Developers can see the AI’s plan, progress, and decisions at any time—making the process transparent and trustworthy.
In AI coding, visibility is not optional—it’s essential for effective collaboration.
Enhanced Context Engineering
We believe better context leads to better code. The key is Enhanced Context Engineering, which includes:
-
Deep codebase understanding: The AI doesn’t just read code—it understands structure, dependencies, and design philosophy.
-
Memory: A persistent record of project history, user actions, and AI interactions, enabling long-term context retention.
By enriching the input context, Qoder delivers more accurate suggestions and provides insights for architectural decisions—going beyond code completion to intelligent co-development.
Enhanced Context Engineering is not just a technical feature—it’s a new development philosophy.
Spec-Driven and Task Delegation
In the age of AI agents, the developer’s primary role shifts from executor to intent clarifier.
Chat Mode: Agent Collaboration
-
You guide the AI via chats.
-
You review, refine, and approve each change.
-
Ideal for short, iterative tasks.
Quest Mode: Autonomous Delegation
-
You write a detailed specification (Spec).
-
You delegate the task to the AI.
-
The AI works asynchronously, only asking for help when stuck.
-
Perfect for long-running, well-defined tasks.
A Spec is more than a task description—it’s a thinking tool and a communication medium. It aligns human and AI goals, acts as a project compass, and becomes part of the team’s knowledge base.
Quest Mode is designed for this new paradigm: write the Spec, delegate the task, and check the results.
Two modes, two collaboration styles:
| Chat Agent Mode | Quest Mode |
|---|---|
| Chat Iteration | Spec First |
| Coding Through Conversation | Delegate Tasks to AI Agent |
| For Short Task | For Long Task |
| Supervise the workflow | Accurate describe the purpose |
The future of development might look like this:
-
Morning: Clarify requirements with stakeholders.
-
Afternoon: Use AI to draft detailed Specs.
-
End of day: Delegate tasks via Quest Mode.
-
Next morning: Review results, refine, and repeat.
Write Specs → Check & Refactor — a new workflow for software development.
Providing the Most Appropriate Model
As the number of available models grows, we asked: "Should choosing the right model be the user’s job?" Our answer is: "No."
Developers need solutions, not model comparisons. They shouldn’t have to study evaluation metrics to pick the best model.
Qoder automatically routes your task to the best model based on complexity and context—ensuring optimal performance without user overhead.
You focus on what to build. We handle how it’s built.
How to Use Qoder to Complete Your Work
Starting a New Project
Qoder has no learning curve. Just describe your idea in natural language.
For example:
- "Create a Spring Boot application for uploading, previewing, and downloading photos."
Qoder will generate the project scaffold and core business logic.
Alternatively, use Quest Mode to first generate a Spec—describing the tech stack, architecture, and initial version. A good initial version is a runnable project.
Adding a Feature to an Existing Project
Most development happens on existing codebases. Before coding, developers need to understand:
-
What the project does
-
Its technical architecture
Repo Wiki provides instant insight. Qoder builds a background index of the codebase and imports it into memory. When you start a task, the context is already prepared—no manual selection needed.
This enables accurate, context-aware assistance from the very first line of code.
Familiar Code Editing with AI Assistance
For daily coding, Qoder supports your workflow with:
-
Code Completion
-
Next Edit Suggestions (NES): Predicts your next change across multiple lines
-
Inline Edit: Edit code directly in the chat
These features integrate seamlessly into your existing habits—enhancing, not disrupting, your flow.
Final Thoughts
Our vision is to solve the real challenges of software development:
-
Make the invisible visible
-
Strengthen knowledge alignment between humans and AI
-
Eliminate technical debt and collaboration friction
-
Free developers from repetitive work so they can focus on innovation
Qoder is available for free during its public preview. We invite you to use it for real-world projects and share your feedback.